Understanding Petechiae Linked to Leukemia

Intro
In the realm of hematology, few indicators are as telling as petechiae. These small, pinpoint hemorrhages often raise red flags pointing to serious underlying conditions, particularly when discussing leukemia. Understanding how petechiae relate to leukemic disorders is essential for medical professionals and students alike. It offers insight into not just leukemia itself, but also the intricate workings of our blood system.
Leukemia is a complex group of cancers affecting the blood and bone marrow. Within these disorders, the role of platelets becomes crucial. When your body’s ability to produce or function platelets gets compromised, various symptoms can arise, one of which is the appearance of petechiae. Grasping this connection is pivotal, and not merely for academic purposes.
Analyzing petechiae in the context of leukemia initiates a discussion about broader hematological issues. This dialogue highlights not just the symptoms but also the diagnostic challenges faced by healthcare providers in the clinical setting.
Through this article, we aim to dissect the relationship thoroughly, exploring areas such as the underlying mechanisms, clinical implications, and the latest diagnostic methodologies.
Preface to Petechiae and Leukemia
Understanding petechiae in the context of leukemia is a vital aspect for both healthcare professionals and patients alike. These small, pinpoint hemorrhages often serve as early indicators of underlying hematological issues, particularly in the realm of blood cancers such as leukemia. Highlighting the interplay between these two essential elements sheds light on their significance in clinical diagnostics and patient management. Knowledge regarding how petechiae manifest, along with their multifactorial origins, can lead to quicker diagnosis and better treatment outcomes.
When discussing petechiae, it is necessary to appreciate their role as more than just superficial symptoms. They can point towards serious conditions, thus emphasising the need for vigilant assessment. For instance, a clinician should be concerned about petechiae when accompanied by other alarming signs such as fatigue or recurrent infections, indicating a potential abnormality in blood cell production.
Moreover, within the scope of leukemia, understanding the various types of the disease is equally imperative. Each type of leukemia presents different mechanisms that can lead to the formation of petechiae. Thus, this exploration prepares a comprehensive groundwork for recognizing how these small, often overlooked spots can be telling signs of a larger, more menacing issue.
As we dive deeper into this article, we'll first define petechiae and then explore the various types of leukemia, investigating their clinical relevance. This groundwork ensures that the reader is equipped with a thorough understanding of the material ahead, thus enhancing clinical acumen and promoting better patient outcomes.
Defining Petechiae
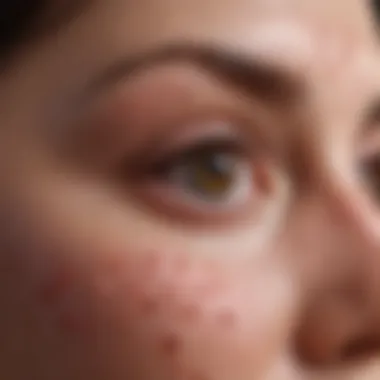
Petechiae are small, round spots that appear on the skin due to bleeding under the surface. They typically measure less than 3 millimeters and can range in color from red, purple, to brown. Their formation occurs when capillaries—tiny blood vessels—break, causing blood to leak into the surrounding tissues. While they may appear insignificant, the presence of petechiae serves as an important diagnostic marker. In the context of leukemia, these spots may signal various underlying abnormalities in blood cells.
Petechiae can present as a rash that might be mistaken for other conditions, making accurate identification critical for clinicians. They are most commonly found on the lower extremities, but can also appear on other areas of the body. Understanding the visual characteristics and locations of petechiae can assist in diagnosis.
Types of Leukemia
Leukemia encompasses a range of blood disorders characterized by abnormal white blood cell production. Let's take a closer look at the different types and their unique features:
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) primarily affects children and is marked by the rapid proliferation of lymphoblasts—immature lymphocytes. One key characteristic of ALL is its propensity to develop rapidly, necessitating immediate and aggressive treatment. Due to this urgency, ALL's contribution to the understanding of petechiae is profound; it can lead to increased bleeding, including petechiae due to bone marrow infiltration which reduces platelet production.
Unlike some chronic forms of leukemia, this type has a higher rate of remission with appropriate therapy, providing a glimmer of hope for affected individuals. However, the rapid progression of ALL means that prompt recognition of symptoms like petechiae can be life-saving.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) has a more insidious onset compared to ALL, primarily affecting older adults. It involves the gradual accumulation of functionally incompetent lymphocytes, leading to a less overwhelming clinical presentation. The progressive nature of CLL can result in symptoms manifesting later, which may complicate the recognition of petechiae as a critical warning sign.
In CLL, the lymphocytes can crowd out normal cells in the marrow, impacting both platelet and red blood cell production. Thus, petechiae are not merely an incidental finding but represent a shift in disease progression.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) stands out due to its more aggressive nature, impacting primarily the myeloid line of blood cells. Those with AML often face rapid symptom development alongside persistent fatigue and infections. The high turnover of immature blood cells can lead to profound cytopenias—especially low platelet counts—which subsequently gives rise to petechiae.
Such visible manifestations signal the urgency of seeking medical attention. Moreover, hematologic abnormalities in AML can complicate the diagnosis, requiring a multifaceted approach to effective treatment.
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) is characterized by a slower increase of myeloid cells in the blood. Patients may live for years with this condition often without severe symptoms, which can mask the presence of petechiae until late in the disease.
A unique aspect of CML is its association with the Philadelphia chromosome, a genetic abnormality found in most patients. This has implications for targeted therapies, which can lead to significant control of the disease, thus potentially reducing the manifestation of symptoms like petechiae.
Understanding these unique features across leukemias is crucial for grasping how they interplay with symptom expressions such as petechiae, establishing the groundwork for better clinical navigation.
Pathophysiology of Petechiae in Leukemia
Understanding the pathophysiology surrounding petechiae in leukemia is crucial to comprehending how these two conditions intertwine. Petechiae, small red or purple spots on the skin, arise from different mechanisms related to blood disorders, particularly in the context of leukemia. An exploration of this subject reveals not just the biological basis, but it also highlights the clinical significance that accompanies the presence of these symptoms.
The occurrence of petechiae often signals disturbances in blood cell production or function. For individuals with leukemia, this can stem from an overaccumulation of malignant cells that disrupt normal hematopoiesis, the process of forming blood cells. Such disruptions impede the production of platelets, which plays a central role in clotting. Thus, recognizing the underlying pathophysiology provides insight into the complexity of leukemia management.
Causes of Petechiae Formation
Platelet Dysfunction
Platelet dysfunction emerges as a pivotal factor in the formation of petechiae in patients with leukemia. This condition refers to a failure of platelets to effectively adhere to blood vessel walls or to aggregate properly when necessary. In the world of cancer care, understanding this dysfunction offers various insights. For one, it shows how leukemia can directly affect platelet production and functionality.


A critical characteristic of platelet dysfunction is its leading role in hemostasis. Without the proper function of platelets, even minor injuries can result in significant bleeding, leading to petechial manifestations. In discussing leukemia, this dysfunction is particularly significant since reduced platelet counts are often observed, correlating directly with bilateral signs of petechiae.
One unique aspect of this dysfunction is how it shapes treatment decisions. Knowing that platelet dysfunction underlies petechiae guides clinicians toward appropriate therapeutic strategies, possibly prioritizing medications that enhance platelet production. However, there's a downside—some treatments might further complicate the issue of platelet aggregation, leading to a delicate balance to strike in managing these patients.
Coagulation Pathway Interruption
Another kernel of understanding lies in the interruption of the coagulation pathways, which also facilitates the development of petechiae in leukemia. These pathways are sophisticated networks enabling blood clot formation. When disruptions occur—be it through disseminated intravascular coagulation, a common feature in aggressive leukemias—the consequence is often petechiae.
The key characteristic of coagulation pathway interruption is its ability to create a challenging environment for proper clotting. For healthcare professionals, recognizing these interruptions not only aids in diagnosis but also in assessing the severity of a patient’s condition. It provides context for why some patients might develop petechiae even when their platelet numbers appear adequate on a complete blood count.
A distinctive feature here is that coagulation pathway interruptions can indicate the severity of leukemia. Thus, clinicians benefit greatly from understanding this relationship when formulating treatment plans. Yet, the downside is that addressing these issues can be multifaceted, often requiring an interdisciplinary approach to care.
Bone Marrow Dysfunction and Hematopoiesis
Moving to the bone marrow's role, this is where everything connects. The marrow is the body’s factory for blood cells, and when leukemia intervenes, it becomes dysfunctional. This dysfunction can lead to a catastrophic failure of healthy blood cell production, with a notable reduction in both healthy leukocytes and platelets.
Hematopoiesis, the process of blood formation, comes under duress in these patients. As leukemia takes hold, the machinery fails to produce sufficient platelets, contributing further to the emergence of petechiae. Understanding the nuances of this dysfunction allows clinicians to tailor interventions that can support or restore normal hematopoiesis, potentially mitigating symptoms such as petechiae.
"A thorough grasp of the pathophysiology not only illuminates the direct connections between leukemia and petechiae but also provides essential insights into effective patient management."
By delving into these areas, we see the intricate dance between leukemia and petechiae. It underscores the importance of targeting both the symptoms and their root causes for patients facing these challenges.
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
Understanding the clinical presentation of petechiae as it relates to leukemia is critical when making a timely diagnosis. Petechiae can often serve as vital signs indicating underlying hematological disorders, particularly leukemia. Their early identification can be a game changer in guiding further diagnostic steps and treatment.
Identifying Petechiae
Identifying petechiae, though sometimes subtle, is key in the diagnostic pathway. These tiny, flat, red or purple spots appear when small blood vessels burst, leading to pinpoint bleeding under the skin.
Visual Characteristics
The visual characteristics of petechiae are especially telling. Typically, these lesions, usually smaller than 3mm, are non-blanching and don't change color when pressed. Their presentation can be distinctive, making them easier to recognize compared to other skin manifestations.
The ability to differentiate petechiae from other skin-related issues is a beneficial choice for this article. For example, bruises may look similar at first glance but typically are larger and change colors over time. Understanding these nuances regarding petechiae offers the advantage of fostering sharper clinical acumen among practitioners or anyone delving into related conditions.
Common Locations on the Body
Common locations where petechiae may blossom include the extremities, particularly around the ankles, as well as on the trunk and sometimes around the eyes. These areas often exhibit a higher degree of fragility in the blood vessel walls due to various factors, thus leading to easy ruptures.
Noting the key characteristic of these locations aids significantly in reaching conclusions about the possible underlying conditions. Recognizing these typical areas can make it simpler for students and professionals to pinpoint the symptoms that warrant further investigation. However, its unique feature lies in how these locations can vary based on age or underlying health conditions, sometimes leading to misdiagnosis if not contextualized correctly.
Diagnostic Techniques
Moving on from identification, proper diagnostic techniques are indispensable in confirming the presence of petechiae linked to leukemia.
Blood Tests and Complete Blood Count
Blood tests, particularly a Complete Blood Count (CBC), play a primary role in evaluating the components of blood. This test measures platelets, red cells, and white blood cells, shedding light on potential abnormalities indicative of conditions such as leukemia. It can unearth issues concerning low platelets, a clear sign that supports the diagnosis of leukemia-related petechiae.
A key characteristic of the CBC is its straightforwardness; it provides an insightful view without necessitating invasive procedures. However, the disadvantage is that it may sometimes yield false negatives, and thus subsequent testing may still be required to confirm findings.
Bone Marrow Biopsy
The bone marrow biopsy emerges as a cornerstone of diagnosis when deeper clarity is required. This procedure involves extracting a small amount of bone marrow to look at the number and quality of blood cells. Understanding the cellular architecture of the marrow can offer invaluable insights into whether leukemic cells are present.
Its distinct characteristic lies in how extensive it can be for reaching a diagnosis. If done correctly, a biopsy can provide definitive answers. However, it does carry the potential downside of discomfort for the patient, making thorough discussion prior to the procedure essential.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging Techniques such as CT scans or MRIs can also play a role. While these imaging modalities are not primary diagnostics for petechiae, they can be helpful in evaluating potential complications that arise from leukemia, like organ enlargement or vessel anomalies.
Their utility stems from the ability to gain a comprehensive view of the patient’s anatomy, giving context to the hematological findings. However, the drawback could be that they might not directly reveal information specifically about petechiae, thus serving a supportive role rather than being a decisive factor in diagnosis.
In summary, effectively identifying petechiae and utilizing appropriate diagnostic techniques significantly impact understanding and addressing leukemia. Fostering knowledge of these aspects sets the groundwork for timely treatment.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is a critical aspect in understanding the connection between petechiae and leukemia. It involves distinguishing one disease entity from another and is fundamental when interpreting clinical presentations. Since petechiae can arise from a variety of conditions, an accurate differential diagnosis ensures that the underlying cause of these small hemorrhages is identified.


Distinguishing Factors for Diagnosis
Making a precise diagnosis often hinges on distinguishing factors that can help differentiate leukemia from other diseases that also present with petechiae. Some of the key factors include:
- Patient History: A thorough review of the patient's medical history can provide crucial insights. Instances of recent infections, bleeding disorders in family members, or exposure to certain chemicals should all be taken into account.
- Physical Examination: Looking for other signs on examinations, such as enlarged lymph nodes or splenomegaly, can help guide the diagnosis.
- Laboratory Findings: Specific blood tests are invaluable. For example, a complete blood count (CBC) revealing low platelet levels may suggest a hematological disorder, whereas a normal count might steer the focus toward another condition.
A careful assessment of these factors allows healthcare professionals to pinpoint whether the underlying cause is leukemia or another disorder, leading to better treatment strategies and outcomes.
Other Conditions Causing Petechiae
When addressing the causes of petechiae, one must consider several other conditions that can lead to similar symptoms.
Vascular Disorders
Vascular disorders can significantly contribute to the appearance of petechiae. These conditions often involve impairments in the blood vessel walls, leading to leakage of blood into surrounding tissues. The key characteristic of vascular disorders is their potential to disrupt circulatory integrity, resulting in localized bleeding spots.
A common example is vasculitis, which involves inflammation of the blood vessels. This can escalate to more severe complications if not treated promptly. The unique feature of vascular disorders is how they manifest—often presenting with other symptoms such as rashes or swelling, making them an important consideration in a differential diagnosis. However, the downside is that the treatment for these disorders can be complex and systemic.
Platelet Disorders
Moving on, platelet disorders represent another category where petechiae can be evident. These conditions usually arise from either decreased platelet production or increased platelet destruction. The hallmark of platelet disorders is a propensity to bleed easily due to insufficient platelets in circulation.
Conditions such as immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) exemplify this aspect. The unique feature here involves the body’s immune system mistakenly attacking its own platelets, leading to significantly reduced counts. While this makes platelet disorders a relevant consideration in petechiae connection to leukemia, they may require distinct management approaches, which could include immunosuppressive therapies.
Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases significantly contribute to the emergence of petechiae. These can range from minor infections to severe conditions that necessitate immediate medical attention. The main characteristic of pathogenic infections is their acute onset and association with fever or systemic symptoms.
Meningococcal infection is a prime example. This condition can quickly escalate and may also lead to sepsis. What stands out about infectious diseases is their potential to cause widespread effects throughout the body, which can complicate diagnosis since they present various symptoms. Treatment typically targets the infection, but distinctive features may blur the lines with leukemic presentations.
Medication Effects
Lastly, medication effects represent an important category where petechiae can occur. Certain drugs, such as anticoagulants or specific antibiotics, can alter clotting mechanisms or platelet function, contributing to hemorrhagic manifestations like petechiae.
The key characteristic of this group is the temporality of symptom onset; petechiae often develop after a new medication is initiated or dosage is altered. A unique feature of medication-related petechiae is sometimes their reversible nature upon discontinuation of the offending agent. However, this can be a double-edged sword, as the underlying condition for which the medication was prescribed may also persist without adequate management.
Identifying these differential diagnoses enriches the discussion around petechiae's role in leukemia and helps sharpen clinical focus on patient evaluation.
Treatment and Management Options
In managing patients with leukemia, particularly those manifesting petechiae, treatment options extend beyond simply addressing superficial symptoms. The key lies in understanding the underlying cause, ensuring the patient not only experiences symptomatic relief but also targets the root of the problem. This comprehensive approach is central to improving outcomes in patients, as it gives life beyond mere management—a pathway toward potential recovery or stabilization.
Addressing the Underlying Cause
Targeted Therapy for Leukemia
Targeted therapy represents a significant advancement in the treatment landscape for leukemia. Unlike traditional chemotherapy, which indiscriminately strikes both cancerous and healthy cells, targeted therapy hones in on the specific genetic mutations or pathways that drive the growth of cancer cells.
The main characteristic of targeted therapy is its precision. By focusing on particular proteins or genes involved in the cancer's growth, these therapies tend to minimize damage to healthy cells, which translates to fewer side effects and a better quality of life for patients. One well-known example includes tyrosine kinase inhibitors for chronic myeloid leukemia, effectively blocking the signals that keep the cancer cells alive.
However, its unique feature lies in the continuous development of new targeted agents as more is understood about the genetic makeup of leukemia cells. This evolving landscape is advantageous, offering patients a more personalized approach to treatment. Yet, it can also be a double-edged sword—these therapies may only be effective in a subset of patients whose tumors possess the specific genetic targets.
Supportive Care Measures
No discussion on managing leukemia would be complete without mentioning supportive care measures. These strategies are critical; they ensure patients maintain a certain quality of life throughout the treatment process. Supportive care includes a variety of interventions, such as blood transfusions, infection prophylaxis, and pain management, tailored to the individual needs of each patient.
The key characteristic of supportive care is its ability to relieve symptoms and side effects without directly addressing the leukemia itself. It's a beneficial choice because it enhances the overall well-being of patients. For instance, patients suffering from anemia can benefit from red blood cell transfusions, directly addressing fatigue and improving their capacity to handle leukemia treatment.
However, while these measures can provide significant relief, they do not halt disease progression. Patients and healthcare providers must weigh these advantages against the reality that supportive care alone won't eradicate the leukemia.
Managing Symptoms Related to Petechiae
Transfusion Strategies
Transfusion strategies specifically target the management of symptoms related to petechiae and associated conditions. When a patient's platelet count is critically low, platelet transfusions can be lifesaving, minimizing the risk of bleeding complications.
A notable characteristic of these strategies is their timeliness; administering transfusions promptly can significantly reduce the risk of severe hemorrhage. Such interventions are popular because they can quickly alleviate symptoms and allow patients to continue their broader treatment regimen without interruption.

One unique feature of transfusion strategies is the careful matching of platelet donors to recipients, which optimizes the effectiveness of the transfusion. However, it is not without its disadvantages; repeated transfusions carry the risk of alloimmunization, where the patient's immune system develops antibodies against transfused platelets, complicating future transfusion efforts.
Patient Education
Education for patients and caregivers is vital in the comprehensive treatment approach. Patient education offers insight into how to recognize and respond to symptoms of leukemia and petechiae, thus empowering individuals to actively engage in their healthcare.
The primary characteristic of strong patient education is its focus on promoting self-management skills. Patients who understand their condition are often better equipped to monitor their health and communicate any changes to their healthcare team swiftly. This proactive knowledge can lead to faster detection of complications or relapses, potentially improving outcomes.
A unique feature of patient education programs includes the use of shared decision-making, where patients collaborate with their healthcare providers to discuss treatment options based on a mutual understanding of risks and benefits. While the benefits of educating patients can be profound, a disadvantage is that not all patients may have equal access to educational resources or understand complex medical concepts, resulting in disparities in patient empowerment.
"Informed patients are more likely able to seize the reins of their health, becoming partners in the journey of their illness."
In summary, addressing treatment and management options in relation to petechiae and leukemia is paramount for a thorough understanding of patient care. By implementing targeted therapies, supportive measures, and emphasizing education, healthcare providers can contribute to enhanced quality of life and better prognosis for those living with these conditions.
Prognostic Implications
In the realm of hematology, understanding the prognostic implications of petechiae in relation to leukemia is crucial for both clinicians and patients alike. These small pinpoint hemorrhages offer more than just a surface-level symptom; they are often harbingers of underlying hematological disruptiveness that could significantly impact patient outcomes. Recognizing how the presence, frequency, and pattern of petechiae can correlate with different types of leukemia can directly influence treatment plans and prognosis.
Life Expectancy and Quality of Life
The intersection between the presence of petechiae and survival rates in leukemia is a potent area of study. Studies have shown that individuals with acute forms of leukemia, characterized by more visible petechiae, might face a steeper decline in life expectancy when compared to those with chronic forms. The density of petechiae often indicates the severity of thrombocytopenia, which is the low platelet count that can complicate not only leukemia but treatment regimens, too.
A patient’s quality of life can also be affected in multifaceted ways:
- Emotional Well-being: Noticing visible marks on the skin can lead to anxiety and stress, which may further complicate treatment adherence.
- Physical Limitations: Symptoms associated with leukemia, especially when compounded by petechiae, can affect everyday activities, making routine tasks feel overwhelming.
- Social Dynamics: The visibility of petechiae may also influence social interactions, as patients may feel self-conscious or stigmatized, leading to social withdrawal.
"Petechiae are not merely symptoms to be observed; they can be key pieces of the larger puzzle in understanding leukemia progression and treatment efficacy."
Role of Early Detection
Catching leukemia at an early stage can make a world of difference, particularly in patients who present with petechiae. The presence of these small hemorrhages can serve as a red flag, prompting further investigation into a patient's hematological health. Early detection not only facilitates timely intervention but also provides more treatment options, which can be crucial in a patient’s journey.
Early identification often leads to:
- Tailored Treatment Plans: When doctors recognize petechiae early on as symptoms of possible leukemia, they can devise treatment protocols that address both the cancer and any associated complications more effectively.
- Improved Monitoring: Patients with a known risk of leukemia and visible symptoms like petechiae can be monitored closely, allowing for prompt adjustments to therapy as needed.
- Enhanced Patient Education: Patients informed about the potential significance of petechiae are more likely to report changes in their symptoms, creating a feedback loop that benefits their care.
In summary, understanding the prognostic implications of petechiae in leukemia not only improves diagnostic accuracy but also fosters a more informed dialogue between healthcare providers and patients, facilitating a more holistic approach to treatment. Delving into the nuances of each patient’s experience is vital, guiding the way toward better outcomes.
Research and Future Directions
Research into the relationship between petechiae and leukemia plays a crucial role in enhancing our understanding of these complex conditions. By investigating the underlying mechanisms of petechiae formation in leukemic patients, researchers can identify specific characteristics that may predict the progression of disease or effectiveness of treatment. Understanding these connections can lead to significant improvements in patient outcomes.
Future studies in this area are not just important from a clinical perspective, but also contribute to the broader field of hematology. The exploration of underlying biological mechanisms gives insights into how the body’s blood-forming processes can go awry, ultimately leading to conditions like leukemia. Here are some key areas of focus for ongoing research:
- Understanding Mechanisms: A deeper dive into how functional impairment of platelets contributes to petechiae could provide valuable insights.
- Patient Stratification: Researching specific patient populations to better tailor treatment could result in more personalized healthcare approaches.
- Longitudinal Studies: Ongoing studies that track patients over time will illuminate how early symptoms such as petechiae influence long-term outcomes.
"Studying the nuances of petechiae can shine a light on the larger mysteries of leukemia and other hematologic disorders."
Ongoing Studies and Clinical Trials
There are several ongoing studies and clinical trials aimed at understanding petechiae in patients with leukemia. These research efforts focus on critical questions, such as the precise mechanisms causing the symptoms and potential biomarkers for disease progression.
- National Cancer Institute (NCI) Trials: The NCI often sponsors trials that assess new treatments that might reduce symptoms or complications of leukemia, particularly concerning symptoms like petechiae.
- Blood Journal Studies: Many peer-reviewed articles publish findings related to blood disorders, and several are currently investigating the correlations between platelet counts and petechiae in leukemia.
- Innovative Treatments: Trials focusing on new medications that can improve platelet function are crucial. This includes examining how these drugs can prevent petechiae in patients undergoing chemotherapy, known for adversely affecting blood cell production.
Potential Advances in Treatment
As the landscape of research evolves, so does the potential for advancing treatment modalities. Innovations in how we understand and treat petechiae related to leukemia can open new doors. Some notable advancements include:
- Targeted Medications: New drugs aimed at enhancing platelet production and function are in development. These specifics are vital for patients who suffer from severe thrombocytopenia due to leukemia treatment.
- Gene Therapy: There's growing interest in using gene therapy approaches to correct underlying genetic issues in patients with inherited blood disorders, which may have a bearing on petechiae development.
- Comprehensive Care Models: Expanding treatment to include integrative care, addressing both physical and psychosocial aspects of living with leukemia, may improve overall quality of life, which is often impacted by the appearance of symptoms such as petechiae.
The continuous investigation will help refine therapeutic strategies, making treatments more effective and personalized. It's a path filled with potential, and as more data emerges, the hope is that effective management strategies for both petechiae and the underlying leukemia will become more refined.
Closure
The exploration of petechiae in relation to leukemia reveals significant insights regarding both understanding and managing potential hematological disorders. Ultimately, this connection emphasizes the importance of recognizing petechiae not merely as superficial symptoms but as possible indicators of underlying malignancies. When a clinician sees these tiny red dots on a patient's skin, it can trigger a cascade of inquiries that lead to early diagnosis and timely interventions.
Summarizing Key Points
In summary, the key takeaways from our discussion include:
- Definition and Description: Petechiae are small, pinpoint hemorrhages that can signal various underlying medical conditions, including leukemia.
- Pathophysiology: The formation of petechiae in patients with leukemia is primarily tied to dysfunctions in the blood's clotting mechanism, arising from disruptions in hematopoiesis and abnormal platelet production.
- Clinical Identification: Spotting petechiae can aid healthcare providers in the correct and prompt identification of potential blood disorders.
- Differential Diagnosis: It is essential to delineate leukemia from other conditions that may present similarly, ensuring appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
- Management Strategies: Managing underlying causes and symptoms is crucial. This can range from targeted therapy for leukemia to supportive measures that help patients deal with persistent symptoms.
The Importance of Ongoing Research
Ongoing research in the field of hematology is vital for several reasons:
- Understanding Mechanisms: Continued studies help us to decode the complexities of blood disorders and their manifestations, including the intricate relationship between petechiae and leukemia.
- Improved Treatment Modalities: As new therapies are investigated, the options available may enhance patient outcomes, moving from a one-size-fits-all approach to more tailored treatments.
- Awareness and Education: Research contributes not only to medical professionals' knowledge but also to broader awareness among patients and the public about the signs of leukemia. Increased awareness can lead to earlier presentations to healthcare facilities and better outcomes.
Ongoing studies promise to illuminate previously murky waters regarding the etiology, diagnosis, and treatment of blood-related disorders.















