Understanding Lower Body Cramping: Causes and Management

Intro
Lower body cramping is a common yet often overlooked issue that affects many individuals. It typically manifests as sudden, involuntary muscle contractions, resulting in significant discomfort or pain. Understanding this phenomenon is crucial not only for those who experience it regularly but also for health professionals who seek effective management strategies for their patients.
This article will provide an in-depth exploration of the causes, physiological mechanisms, and potential implications of lower body cramps. Through this understanding, readers can become better equipped to recognize the symptoms, pinpoint underlying causes, and implement practical management strategies. By focusing on evidence-based practices, we aim to enhance awareness and promote a proactive approach to addressing lower body cramping.
Importance of the Research
The implications of lower body cramping extend beyond mere discomfort. It can indicate underlying health issues, impact overall physical function, and affect quality of life. Recognizing the importance of this topic is vital in fostering a healthier, more informed population.
Results and Discussion
Presentation of Findings
Through the examination of peer-reviewed studies, we found a range of factors contributing to lower body cramping. These include dehydration, nutrient deficiencies, overexertion during physical activity, and even certain medications. Each cause can lead to different manifestations of cramps, often requiring targeted approaches for relief.
Implications of Results
The understanding of lower body cramping has significant implications for various groups, including athletes, elderly populations, and those with sedentary lifestyles. The management of cramps often involves lifestyle modifications, such as optimizing hydration, adjusting dietary intake, and incorporating adequate stretching and warming up before strenuous activities.
Furthermore, the connection between cramping and medical conditions, such as diabetes or circulatory issues, cannot be ignored. Early recognition and appropriate interventions can reduce both frequency and severity of cramps, improving overall well-being.
"Lower body cramps are not merely a nuisance; they can be indicators of larger health issues that require attention."
In summary, this article endeavors to educate readers on lower body cramping by unraveling its complexities and providing actionable strategies for relief and prevention. By fostering a deeper understanding, we hope to empower individuals to take control over their health regarding this common issue.
Intro to Lower Body Cramping
Understanding lower body cramping is essential in both clinical and everyday contexts. Muscle cramps can be sudden and painful, impacting daily life, exercise performance, and overall well-being. Awareness of cramping can guide individuals in identifying when they might need to make lifestyle changes or seek medical advice. Furthermore, comprehending the root causes and mechanisms behind these cramps fosters proactive management and prevention strategies, crucial for maintaining one's health and activity levels.
Definition and Significance
Lower body cramping refers to involuntary muscle contractions in the legs, thighs, and calves. These spasms can occur unexpectedly and may last from a few seconds to several minutes. The significance of these cramps lies not only in their discomfort but also in their potential to signal underlying health issues. Frequent cramps can indicate dehydration, mineral deficiencies, or nerve dysfunctions, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and evaluation. Understanding the definition and significance of lower body cramps helps caregivers and affected individuals to take appropriate preventive and proactive steps.
Prevalence in Different Populations
Muscle cramps impact a diverse range of populations, with variations in frequency and severity. Certain groups are more prone to these episodes. For example, athletes and individuals who engage in high-intensity physical activities often experience exercise-induced cramps. Additionally, older adults experience nocturnal leg cramps at higher rates due to physiological changes associated with aging. Pregnant women are another notable demographic, facing increased cramping due to hormonal changes and extra weight. Understanding the prevalence of lower body cramps in different populations allows for a tailored approach to education and management strategies, ensuring that vulnerable groups receive the attention they need.
Physiology of Muscle Cramping
The physiology behind muscle cramping is complex and critical to understanding how these events occur in the lower body. This section emphasizes the interplay between muscle function, structure, and the nervous system's role in inducing cramps. By unpacking these mechanisms, we can better appreciate the biological nuances that contribute to muscle cramps and their implications for health and physical performance.
Muscle Function and Structure
Muscles are composed of fibers that contract to produce movement. Each muscle fiber contains proteins, such as actin and myosin, that interact during muscle contraction. This process relies on energy, mainly derived from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) produced through metabolic pathways. When muscles experience stress, such as during intense exercise or long periods of inactivity, this process can become disturbed.
Typically, muscle cramping is a result of excessive stimulation or changes in the biochemical environment within these fibers. Factors like dehydration can lead to electrolyte imbalances, affecting the balance of sodium, potassium, and calcium which are essential for muscle contraction and relaxation. When these minerals are out of balance, the regulation of muscle contraction is impaired, leading to involuntary spasms.
Important Note: Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet are critical to prevent cramps by supporting muscle function.
Understanding the structure of muscles aids in grasping why cramps happen. Muscles are anchored to bones at tendons and are divided into various groups that serve different functions, such as flexion and extension of joints. Fatigue in these muscle groups due to overexertion can trigger cramps, as the body reacts to prevent injury or overuse.
Nervous System's Role
The nervous system plays a vital role in the control of muscle contractions. Nerves transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles, coordinating movement and triggering contractions. During cramping, the nerve pathways can become overactive. This can occur due to several reasons, such as heightened physical activity, stress, or even underlying medical conditions that affect nerve health.
The excitation of motor neurons leads to muscle fibers contracting uncontrollably. In scenarios where fatigue sets in, the ability of motor neurons to regulate muscle contractions deteriorates, increasing the likelihood of cramping. Additionally, changes in the central nervous system, often linked to stress or fatigue, can exacerbate the risk as the body struggles to maintain muscular control.
Moreover, certain conditions like diabetes or neuropathies can influence nerve function, further complicating the situation. The intricate relationship between muscle health and nervous system activity underscores the need for a holistic approach to preventing and managing cramps.
In summary, a clear understanding of muscle function, structure, and the nervous system's role is crucial when approaching the problem of muscle cramping in the lower body. This foundation can enhance our strategies for prevention and treatment.
Types of Lower Body Cramps
Understanding the different types of lower body cramps is crucial for both diagnosis and management. Each type can have unique features, causes, and implications for individuals. Knowledge about these distinctions allows for more targeted preventive and therapeutic strategies. This section will explore three common types of cramps: Nocturnal Leg Cramps, Exercise-Induced Cramps, and Thigh and Calf Spasms. Each type presents varying challenges and requires a differing approach to management.
Nocturnal Leg Cramps
Nocturnal leg cramps are involuntary muscle contractions that occur during nighttime, often causing significant discomfort. They tend to affect the calf muscles and can disrupt sleep, leading to fatigue during the day. Characteristically, these cramps can last from a few seconds to several minutes. The exact cause of nocturnal leg cramps is not always clear but may relate to factors like dehydration, prolonged sitting, or certain medications.
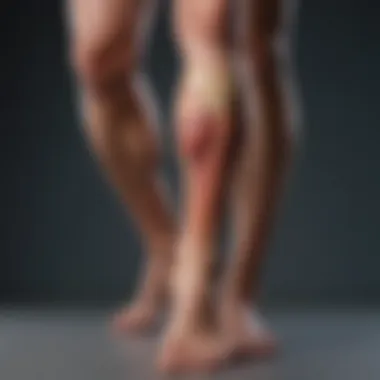
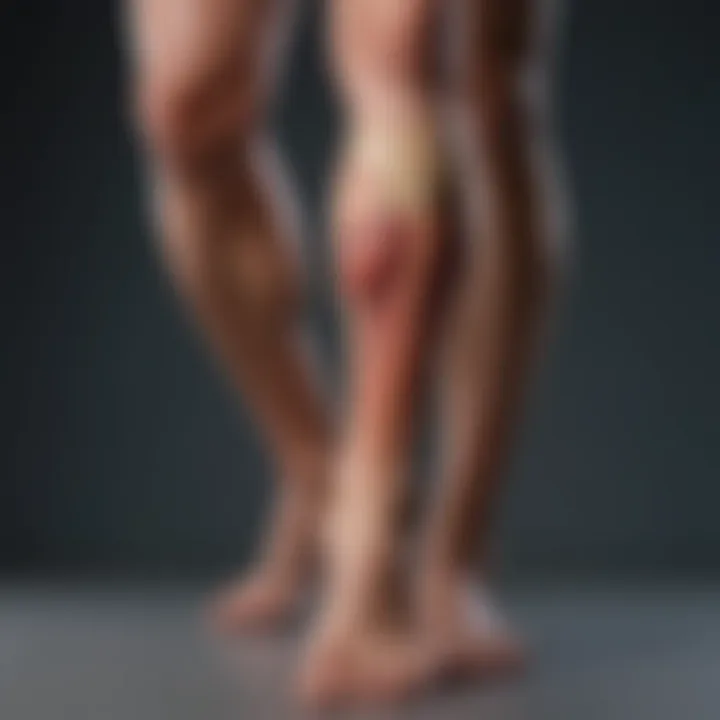
Implications of Nocturnal Leg Cramps:
- Sleep disturbance: Frequent cramps can lead to inadequate sleep, affecting overall health.
- Physical pain: The intensity of the cramps can result in residual soreness or discomfort.
- Emotional stress: Repeated episodes may cause anxiety regarding sleep and contribute to stress.
Exercise-Induced Cramps
Exercise-induced cramps occur during or after physical activity. They are quite common among athletes but can also affect non-athletic individuals engaging in strenuous activities. These cramps generally occur in muscle groups being used most heavily during the activity, such as calves or thighs. Possible triggers include dehydration, fatigue, and inadequate warm-up routines.
Understanding Exercise-Induced Cramps:
- Prevalence in athletes: This type is frequently reported among runners, cyclists, and other sports participants.
- Hydration and nutrition: Electrolyte imbalances and poor diet can contribute to the severity of these cramps.
- Preventive measures: Adequate warm-ups, hydration, and flexibility exercises can help reduce occurrence.
Thigh and Calf Spasms
Thigh and calf spasms are specific contractions in the thigh or calf muscles. These spasms can occur spontaneously, often leading to sharp and sudden pain. The underlying causes for these spasms can vary widely and might include excessive exertion, dehydration, or insufficient muscle conditioning.
Key Aspects of Thigh and Calf Spasms:
- Sudden onset: Can be unexpected, impacting activities or workouts.
- Causes vary: May result from overuse or nutritional deficiencies, leading to muscle strain.
- Management strategies: Stretching and adequate recovery time can improve muscle resilience.
Understanding the types of cramps is vital for effective management. Insights into their causes, implications, and treatment options can enhance quality of life for affected individuals and provide pathways for preventive measures.
Common Causes of Lower Body Cramps
Understanding the common causes of lower body cramps is crucial for individuals experiencing this discomfort. Identifying these causes can lead to better management strategies, potentially reducing the frequency and severity of cramps. Cramps can disrupt daily activities and impact quality of life, making awareness of the underlying reasons essential. Addressing causes proactively can offer relief and improve overall well-being.
Dehydration and Electrolyte Imbalance
Dehydration is a significant contributor to muscle cramping. When the body loses fluids through sweat or insufficient intake, it can disrupt the balance of electrolytes. Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium, play pivotal roles in muscle function. An imbalance can lead to the involuntary contraction of muscles, resulting in cramps.
To prevent dehydration, it is essential to stay adequately hydrated, particularly during intense physical activity or hot weather. Here are some useful strategies:
- Drink water regularly throughout the day.
- Consider electrolyte solutions during prolonged exercise.
- Pay attention to thirst cues and consume fluids before feeling dehydrated.
Mineral Deficiencies
Certain mineral deficiencies may also trigger lower body cramps. Potassium, calcium, and magnesium are vital for muscle contraction and relaxation. A lack of these minerals can lead to increased susceptibility to cramps. Diets lacking in these essential nutrients can cause physiological imbalances in muscle health.
Incorporating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and dairy can help maintain adequate mineral levels. Individuals should consider the following dietary sources:
- Potassium: Bananas, oranges, spinach.
- Calcium: Dairy products, leafy greens.
- Magnesium: Nuts, seeds, whole grains.
Overexertion and Fatigue
Overexertion during physical activities can easily lead to muscle fatigue and subsequent cramping. Strenuous exercise challenges the body and can lead to fatigue when proper recovery is not observed. Athletes and individuals engaging in prolonged or intense physical activity may find they are at higher risk for cramps due to muscle overuse.
To minimize the risk of cramps associated with overexertion, individuals should:
- Gradually increase the intensity of workouts to allow for adaptation.
- Engage in proper warm-up and cool-down routines.
- Allow sufficient rest and recovery time between workouts.
Recognizing these common causes of lower body cramps can aid in preventing future episodes and reducing discomfort. Each factor is interconnected and requires careful consideration to manage effectively. Increasing awareness about hydration, nutrition, and exercise can lead to a more holistic approach in addressing lower body cramping.
Risk Factors for Muscle Cramps
Understanding the risk factors for muscle cramps is vital for effective management and prevention. Identifying these factors can help individuals recognize when they might be at higher risk and enables them to take proactive steps. Muscle cramps can significantly impact daily life and physical activity, making it essential to understand who is more susceptible and why.
Age and Gender Considerations
Age and gender play critical roles in the prevalence of muscle cramps. Studies indicate that older adults are more prone to experiencing cramps due to reduced muscle mass and decreased flexibility. As individuals age, their body undergoes various changes that can affect muscle function. Additionally, hormonal differences can also contribute to variations in cramping patterns between genders. For instance, women may experience more cramps during hormonal fluctuations, such as during menstruation.
These insights reveal that preventive measures may need to be tailored, taking age and gender into account. Strength training and flexibility exercises can be particularly beneficial for older adults. Awareness of how these factors influence cramping can empower individuals to adjust their routines accordingly.
Physical Activity Levels
Physical activity levels are another significant factor affecting the likelihood of muscle cramps. Engaging in high-intensity activities can lead to overexertion, particularly in individuals who are not used to such exertion. This is especially relevant for athletes or those participating in strenuous workouts. The body may respond to this stress with cramps as a warning sign of fatigue or strain.
On the other hand, a sedentary lifestyle can also predispose individuals to cramping. Lack of movement can result in weak muscles and poor blood circulation, increasing the risk for cramps during unexpected physical activity. Balancing activity levels is crucial; both overexertion and inactivity are potential triggers for muscle cramps.
"Physical activity should be approached with gradual intensity to avoid cramping."
Strategies like gradually increasing activity intensity can greatly reduce the chances of muscular cramping. Regular, moderate exercise fosters muscle strength and endurance, helping to manage and mitigate cramps.


Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can heighten the risk of muscle cramps. Disorders such as diabetes, neuropathy, and thyroid issues may impair normal muscle function, leading to an increased incidence of cramps. Conditions that affect hydration or circulation, such as heart disease or kidney dysfunction, can also contribute.
Individuals with chronic illnesses should consult healthcare providers for tailored management strategies that address both their condition and the risk of cramps. Regular monitoring and appropriate treatment can make a significant difference in the frequency and severity of muscle cramping episodes.
In summary, addressing risk factors like age, gender, physical activity levels, and underlying medical conditions is essential. By gaining a clear understanding of these elements, individuals can better model their lifestyles to prevent muscle cramps effectively.
Implications of Chronic Cramps
Understanding the implications of chronic cramps is essential for those affected. Chronic cramps are not merely a passing discomfort; they can significantly disrupt one’s quality of life. Frequent muscle spasms may signal underlying issues that require attention. The importance of addressing chronic cramps cannot be underestimated, as their effects can extend beyond physical pain to influence emotional well-being and daily functioning.
Impact on Daily Activities
Chronic cramps can severely impact daily activities. Simple tasks, such as walking or standing, may become excruciating experiences. Individuals may alter their routines to avoid triggering a spasm, leading to decreased mobility. This reduction in physical activity often compounds the problem. With less movement, muscular strength can decline. In turn, this may lead to a cycle of increased cramping due to weakened muscles.
Furthermore, people may find themselves waking at night due to spasms, resulting in disrupted sleep patterns. Poor sleep can affect concentration, mood, and overall health. As a result, chronic muscle cramps indirectly influence job performance and social interactions. Individuals may feel reluctant to participate in activities they once enjoyed, leading to social isolation. Identifying effective management strategies can alleviate these burdens.
Psychological Effects
The psychological ramifications of chronic cramps deserve careful consideration. Persistent muscle spasms can lead to anxiety and frustration. The unpredictability of when a cramp may strike adds stress to everyday situations. Such stress can foster a heightened awareness of one's body, leading to a state of constant vigilance. This hyperawareness can reduce one’s ability to relax, thereby increasing the perception of pain.
Additionally, the emotional toll of living with chronic cramps can lead to feelings of helplessness. When individuals feel that their physical condition controls their lives, they may develop a negative perception of their physical capabilities. This adverse mindset can compound feelings of depression. It is vital for healthcare providers to incorporate psychological support into treatment plans for those suffering from chronic cramps.
Chronic cramps not only affect the body but also the mind. Addressing both dimensions is crucial for recovery.
To summarize, the implications of chronic cramps extend beyond physical discomfort. They negatively influence daily activities and psychological well-being. Recognizing these factors can lead to more comprehensive management strategies that enhance overall quality of life.
Preventive Strategies for Lower Body Cramps
Lower body cramps are a prevalent issue that can significantly impact a person's quality of life. Preventive strategies are essential, as they empower individuals to take proactive measures against the onset of cramps. Implementing these strategies not only reduces the frequency and severity of cramps but also enhances overall well-being. This section will discuss key component—hydration practices, nutrition and diet adjustments, and the incorporation of stretching and strengthening exercises. Each of these strategies contributes uniquely to preventing lower body cramps through different physiological pathways.
Hydration Practices
Adequate hydration is a cornerstone of muscle function. When the body is dehydrated, the risk of muscle cramps increases. Water plays a critical role in maintaining electrolyte balance, which is vital for muscle contractions and overall muscular health. Among the electrolytes, sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium are particularly important.
To maintain optimal hydration, individuals should aim to drink water consistently throughout the day, not just during physical activity. The amount of water required can vary depending on factors such as age, weight, activity level, and climate. As a guideline, a daily intake of around 2 to 3 liters for adults is often recommended. Here are some key points to consider about hydration:
- Drink water before, during, and after exercise to replenish fluid lost through sweat.
- Consider electrolyte drinks during prolonged physical activities to restore minerals lost.
- Monitor urine color as an indicator of hydration status; pale yellow suggests good hydration, while dark yellow indicates dehydration.
Nutrition and Diet Adjustments
Dietary choices have a profound impact on preventing muscle cramps. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is important for maintaining muscle health. Focus on nutrients that support muscle function. Foods high in potassium include bananas, oranges, and spinach, while dairy products provide calcium. Magnesium can be found in nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
To optimize nutritional intake, consider the following recommendations:
- Incorporate a variety of fruits and vegetables into daily meals. Aim for colorful options to cover a broad spectrum of nutrients.
- Ensure an adequate intake of whole grains, legumes, and healthy fats to support overall health and energy levels.
- Avoid excessive caffeine and alcohol as they can lead to dehydration and may exacerbate cramping issues.
Incorporation of Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Regular exercise focusing on stretching and strengthening is an important preventive measure against muscle cramps. Stretching helps to increase flexibility and may reduce the chances of involuntary contractions in the muscles. Likewise, strengthening exercises help build resilience in muscle fibers, making them less prone to cramping. Incorporating these practices into a regular routine can create a foundation for better muscle health.
- Stretch major muscle groups, especially those most prone to cramping, such as calves, hamstrings, and quadriceps. Hold stretches for 15 to 30 seconds.
- Integrate strengthening exercises like squats and lunges to improve muscle endurance and support.
- Explore gentle activities like yoga or pilates that emphasize stretching and core strength, which can further enhance muscle stability.
In summary, implementing effective preventive strategies can lead to a significant decrease in the incidence and intensity of lower body cramps. Through hydration, nutrition, and exercise, individuals can take control of their muscular health, fostering a more active and comfortable lifestyle.
Treatment Options for Existing Cramping
Effective management of lower body cramps is essential for those who experience this discomfort frequently. Treatment options not only focus on alleviating the immediate sensations of cramping but also aim to address underlying causes. Having a clear understanding of these options can empower individuals to take actionable steps in managing their symptoms and improving their overall quality of life.
Immediate Relief Techniques
Immediate relief techniques are critical for reducing the intensity and duration of cramps. These strategies can often be employed at home or in daily life. Here are some common methods:
- Stretching: Gentle stretching of the cramped muscle can help alleviate tension. For example, extending the calf muscle by standing on a step or gently pulling the toes upward can be effective.
- Heat Application: Applying a warm towel or heating pad to the affected area can relax the muscle and promote blood flow. This method is particularly useful for nocturnal leg cramps.
- Cold Therapy: In contrast, if someone experiences a recent cramp, applying ice may help reduce muscle inflammation.
- Massage: Gently massaging the cramped muscle can help. This action may improve circulation and reduce pain.
These techniques, while straightforward, can provide significant relief. They allow for quick responses to cramping episodes, making daily activities more manageable.
Medical Interventions and Therapy
For those with frequent or severe cramps, medical interventions and therapy options are worth consideration. Depending on the underlying cause, several approaches can be taken:


- Physical Therapy: Engaging with a physical therapist can be beneficial. They may provide targeted exercises aimed at strengthening and stretching specific muscles that often cramp.
- Medications: In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications to manage muscle cramps. Muscle relaxants or medications to improve circulation could be helpful, depending on individual health needs.
- Nutritional Supplements: A review of one's dietary intake may reveal deficiencies. For example, supplements containing magnesium or potassium may be advised if tests show deficiencies in these minerals.
- Addressing Underlying Health Conditions: If cramps are linked to conditions like diabetes or thyroid issues, proper treatment and management of those conditions can also reduce cramping episodes.
Seeking medical advice is essential, as persistent cramps can sometimes indicate a more serious underlying condition.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing when to seek medical attention for lower body cramps is crucial for effective management and long-term health. Many individuals experience occasional cramps, often linked to factors like dehydration or fatigue. However, persistent or severe cramps may indicate underlying medical issues that require professional intervention. By understanding the signs that necessitate immediate evaluation, patients can better protect their health and mitigate complications that arise from neglect.
Identifying Serious Symptoms
Identifying serious symptoms is essential in distinguishing between common cramps and those that may signal a more serious condition. Key indicators include:
- Severe Pain: While cramps can be uncomfortable, intense, incapacitating pain that does not subside may require immediate assessment.
- Duration: Cramps that persist for an extended period, lasting longer than a few minutes, should raise concern.
- Swelling and Redness: Accompanying symptoms such as swelling or redness in the affected area can denote a hematoma or thrombosis.
- Weakness or Numbness: Unexplained weakness or numbness in the legs may suggest nerve or circulation issues.
- Systemic Symptoms: Fever, chills, or unexplained weight loss in conjunction with cramps may indicate infection or other systemic problems.
It is advisable to monitor symptoms and seek medical guidance when these signs arise, as early intervention can prevent further complications.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
The significance of an early diagnosis cannot be overstated. Timely medical intervention can lessen the risk of complications, facilitate appropriate care strategies, and enhance recovery. Early diagnosis often leads to:
- Targeted Treatment Plans: Identifying the root cause of cramps allows healthcare providers to develop strategies tailored to the individual’s needs. This could involve lifestyle, dietary adjustments, or specific medications.
- Avoiding Chronic Issues: Addressing cramping early may prevent recurrent or chronic muscle issues which can interfere with quality of life and daily activities.
- Improved Quality of Life: Managing symptoms promptly can lead to enhanced mobility and less overall discomfort, thereby improving day-to-day function.
Consulting with a healthcare professional when experiencing worrisome symptoms ensures a comprehensive evaluation. With clear communication about their symptoms, patients can aid in receiving accurate diagnoses and effective treatment.
"Always prioritize your health by being proactive. Ignoring symptoms might lead to escalated health issues."
Ultimately, recognizing when to seek medical attention is vital for anyone experiencing lower body cramping, especially those who face recurrent incidents. Proper education, awareness, and timely medical consultations are all critical elements in successfully managing this common yet sometimes serious issue.
Evidence-Based Research on Lower Body Cramps
In the realm of health studies, evidence-based research stands as a cornerstone. This is especially true when analyzing lower body cramps, which impact many individuals across various demographics. Research provides clarity on the underlying mechanisms of cramping, the contributing factors, and effective management strategies. By grounding practices in accurate data, both education and treatment can become more effective.
The significance of evidence-based research lies in its ability to distill complex physiological phenomena into comprehensible information. This clarity assists in identifying the range of cramping issues from simple, intermittent leg cramps to more severe, chronic conditions. It allows health professionals and educators to pinpoint the most effective prevention methods and treatments, guiding others toward better health outcomes.
Review of Current Literature
The body of literature on lower body cramps is extensive but not uniformly conclusive. Recent reviews have shown a variety of factors contributing to cramping, including dehydration, nutrient deficiencies, and overexertion. One notable study highlights a correlation between low hydration levels and increased incidents of cramping during physical activity. Additionally, literature points to the role of minerals like potassium and magnesium in muscle function, suggesting that an imbalance can lead to higher susceptibility to cramps.
- Dehydration - A significant risk factor as fluids keep the muscles functioning optimally.
- Electrolyte Imbalance - Disruptions in sodium and potassium levels can hinder muscle contractions.
- Muscle Fatigue - Overworked muscles are at a higher risk for spasms.
Research indicates that incorporating proper hydration and ensuring a balanced diet can mitigate these risks. Further exploration of these factors can enhance the efficacy of interventions designed to reduce cramping.
Insights from Clinical Studies
Clinical studies provide valuable insights into the treatment options available for those suffering from lower body cramps. These studies often utilize controlled environments to assess the effectiveness of various interventions, from stretching exercises to nutritional supplementation. For instance, trials have demonstrated that implementing specific stretching routines can significantly decrease the frequency of cramps in active individuals.
Furthermore, some studies indicate that supplementation with specific minerals can also reduce the incidence of muscle cramps. This emphasizes the need for personalized approaches to treatment, pointing out that what works for one group may not be effective for another. The knowledge derived from these studies shapes recommendations for healthcare providers, allowing them to tailor interventions more precisely.
"Understanding the role of evidence-based research is essential for developing effective strategies for managing cramping."
In summary, cultivating a strong foundation of evidence-based research on lower body cramps is essential for professionals and educators alike. By synthesizing information from current literature and clinical findings, the medical community can better approach both prevention and treatment. This ultimately leads to a more informed understanding of the causes of cramping and how best to address them.
Culmination and Future Directions
In this article, the examination of lower body cramping has revealed significant insights into its causes, effects, and management strategies. Understanding the multi-faceted nature of this issue is crucial for individuals who experience such cramps, healthcare professionals, and researchers. The interplay between hydration, nutritional balance, physical activity, and medical conditions underscores the complex challenges people face.
As summarized, lower body cramps can arise from various factors, including dehydration, mineral deficiencies, and muscle fatigue. Furthermore, the implications on daily activities can be quite severe, impacting both physical and psychological well-being. These key findings highlight the need for a holistic approach in addressing this condition.
The importance of ongoing research cannot be understated. Areas such as the efficacy of dietary interventions, personalized exercise programs, and the genetic predisposition to muscle cramps warrant deeper exploration. Insights drawn from future studies can better inform best practices for prevention and treatment.
To optimize strategies for managing lower body cramps, further investigations are essential. Collaboration among nutritionists, medical professionals, and exercise researchers will foster a comprehensive understanding of this phenomenon. Ultimately, this will contribute not just to individual care but also to public health initiatives aimed at reducing the prevalence and impact of lower body cramping.
Summary of Findings
This review has highlighted critical aspects regarding lower body cramping. The type of cramps experienced can vary notably, from nocturnal leg cramps to exercise-induced calf spasms. Key findings include:
- Common Causes: Dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and mineral deficiencies can lead to cramping.
- Risk Factors: Considerations such as age, level of physical activity, and underlying medical conditions play a role in susceptibility.
- Management Strategies: Both lifestyle adjustments and medical interventions are effective in addressing symptoms.
Overall, the knowledge gained from this review serves as a foundation for individuals looking to mitigate the effects of lower body cramps.
Potential Areas for Further Research
Looking ahead, multiple avenues may advance the field of study surrounding lower body cramps. Suggested areas include:
- Etiological Studies: Understanding specific triggers for muscle cramps can provide clarity to those affected.
- Longitudinal Studies: Tracking individuals over time will help identify patterns and more accurately describe the chronic nature of cramps.
- Nutritional Impact: Investigating how various dietary supplements affect muscle cramping could lead to new preventive recommendations.
Researching these areas will not only deepen understanding but also refine approaches to education and treatment, ultimately improving quality of life for those at risk.















