Understanding and Managing Bartholin Cysts: A Guide


Summary of Objectives
This article aims to thoroughly investigate Bartholin cysts, highlighting their etiology, clinical presentation, and relevant management strategies. Understanding the pathophysiology of these cysts is crucial for effective treatment and patient care.
Importance of the Research
Bartholin cysts can significantly affect a woman's quality of life, leading to discomfort and potential complications. Therefore, researching their underlying causes and treatment options provides vital knowledge for those affected.
Intro
Bartholin cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form near the vaginal opening. They originate from the Bartholin glands, which are responsible for secreting fluid that aids in lubrication during sexual activity. These cysts typically develop when the duct of the gland becomes blocked, leading to an accumulation of fluid.
While some patients remain asymptomatic, others might experience discomfort, pain, or even infection. Understanding the nature of Bartholin cysts is crucial for individuals who wish to mitigate their effects and manage any arising symptoms effectively.
As individuals seek knowledge on this common yet often misunderstood condition, it is essential to explore both conservative and surgical management options. This article is crafted for students, researchers, educators, and healthcare professionals who need in-depth insights into Bartholin cysts.
Nature of Bartholin Cysts
Bartholin cysts can manifest due to various reasons. The blockage of the gland's duct often results from cyst formation, trauma, infection, or inflammation. It's estimated that around 2% of women will experience a Bartholin cyst at some point in their lives.
The symptoms vary widely among women. Some may have no noticeable symptoms, while others might face complications that influence their daily activities.
Understanding these cysts begins with awareness of the risks factors and physical manifestations, enabling individuals to recognize when they may require medical attention.
"Early diagnosis and management of Bartholin cysts can prevent complications and improve patient outcomes."
Clinical Presentation
Symptoms
Common symptoms associated with Bartholin cysts may include:
- A noticeable lump near the vaginal opening
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic region
- Changes in urination or bowel movements
- Redness and swelling, signifying potential infection
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional. They may assess the size, tenderness, and characteristics of the cyst. Imaging or further tests may be necessary if complications are suspected, especially if malignancy is a concern.
Management Options
Both conservative and surgical options exist for managing Bartholin cysts. The choice largely depends on symptoms, severity, and patient preferences.
Conservative Treatments
- Sitz baths: Warm baths can alleviate discomfort.
- Pain relief medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers may help reduce symptoms.
Surgical Treatments
- Marsupialization: This common surgical procedure creates an opening for drainage, preventing recurrence.
- Excision: In cases of severe complications or recurrent cysts, complete removal of the cyst may be necessary.
The effectiveness and risks of each method vary, and discussions with a healthcare provider can help patients determine the best approach for their individual circumstances.
Preface to Bartholin Cysts
Bartholin cysts represent a common, yet often misunderstood, condition affecting many women. The purpose of understanding these cysts is not just to identify their symptoms but also to grasp their implications on women's health and wellbeing. Bartholin glands, located at the vaginal opening, play a crucial role in lubrication. When these glands become blocked, cysts may form, leading to discomfort or other complications.
The relevance of this section cannot be overstated. Knowledge about Bartholin cysts aids in early identification and effective management. Many individuals may experience anxiety when facing unexpected medical issues, particularly those related to reproductive health. Informing oneself about the anatomy, causes, and symptoms associated with these cysts can significantly lessen such fears, essentially empowering individuals to take control of their health.
As we delve deeper into the anatomy and functionality of the Bartholin glands, we will explore not only the cysts themselves but also the broader context of women's health. Understanding these aspects fosters a holistic view that benefits both patients and healthcare providers alike.
Overview
Bartholin cysts are fluid-filled sacs that occur when the ducts of the Bartholin glands become obstructed. This obstruction can be caused by various factors including infections, trauma, or hormonal changes. Often, these cysts are asymptomatic and may go unnoticed, but when they become large or infected, they can lead to significant discomfort. Treatment can vary based on the severity of symptoms and the patient's overall health.
Clinicians often recommend monitoring small, asymptomatic cysts without immediate intervention, while more serious cases may require medical or surgical management. Understanding the characteristics and potential complications of Bartholin cysts is essential for women’s health knowledge.
Anatomy of Bartholin Glands
The Bartholin glands, also known as greater vestibular glands, are two small structures located bilaterally at the vaginal opening. Each gland is approximately the size of a pea and is responsible for providing lubrication during sexual arousal. The ducts from these glands open into the vaginal vestibule, contributing to moisture essential for sexual activity.
The normal function of these glands is crucial for female sexual health. Understanding their placement and role can help in identifying problems when they arise. When the ducts become blocked, fluid accumulates, turning into a cyst, which may lead to complications such as pain or infection.
Causes of Bartholin Cysts
Understanding the causes of Bartholin cysts is vital for both diagnosis and treatment. By identifying the factors that contribute to cyst formation, one can better appreciate the mechanisms at play and make informed decisions regarding management. The root causes can typically be categorized into three distinct areas: blockage of the glands, infections, and other contributing factors. Each area sheds light on the potential triggers and risk factors, creating a comprehensive understanding essential for effective patient education and care.
Blockage of Glands

The primary cause of Bartholin cysts often stems from a blockage in the Bartholin glands. These glands are located near the vaginal opening, and their primary function is to produce a lubricating fluid. When the ducts that connect the glands to the vaginal canal become obstructed, fluid builds up within the gland. This can occur due to a variety of reasons. One common reason is that a small cyst can form when mucus, rather than draining, becomes trapped. This accumulation leads to a noticeable swelling.
Blockage could also result from activities such as sexual intercourse, which might temporarily obstruct the ducts. Furthermore, the hormone fluctuations in women, particularly during menstruation, can influence gland function and potentially lead to blockage. Recognizing these blockages is crucial, as they may lead to additional complications if not addressed promptly.
Infections
Infection plays a significant role in the development of Bartholin cysts. Bacterial infections can cause inflammation in the Bartholin glands, making them more prone to blockages. Two common types of infections linked to this condition are sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and non-specific bacterial infections. STIs like gonorrhea and chlamydia can severely affect the glands, leading to cyst formation.
When an infection occurs, it can trigger an inflammatory response that not only complicates the cyst but may also lead to the formation of an abscess. This presents a more severe scenario, as an abscess can cause significant pain and discomfort. Early identification of infections is important, as timely treatment can prevent further complications and improve outcomes.
Other Contributing Factors
A range of additional factors may contribute to the formation of Bartholin cysts. Hormonal changes, for instance, can have a profound effect on gland function. Conditions such as menopause or hormonal therapies may impact how the glands produce fluids and their overall function. Moreover, trauma or injury during childbirth or other pelvic procedures may create an environment susceptible to cyst formation.
Additionally, some medical conditions, including conditions that cause changes in vaginal pH or bacterial flora, can also play a role in increasing the likelihood of cysts forming. Understanding these factors not only enriches one's knowledge of Bartholin cysts but also emphasizes the importance of preventative measures and education regarding sexual health.
It is crucial for individuals to recognize any changes in their reproductive health and seek medical guidance promptly if abnormalities arise.
Recognizing the causes of Bartholin cysts empowers individuals to take charge of their health. Awareness of potential blockages, infections, and other contributing factors is an essential step towards effective management and treatment.
Identifying Symptoms
Identifying symptoms of a Bartholin cyst is crucial for understanding the condition and making informed decisions regarding management. Recognizing the early signs can lead to appropriate treatment, reducing discomfort and potential complications. The symptoms can vary significantly depending on the size of the cyst and whether an infection is present. This section aims to provide clarity on what individuals should observe and when to seek further medical help.
Common Indicators
Awareness of common indicators is the first step in managing a Bartholin cyst. Patients may experience a variety of symptoms:
- Swelling: The most noticeable symptom of a Bartholin cyst. This swelling can vary in size and may present asymmetrically.
- Pain or Discomfort: Patients might feel pain or tenderness in the region, especially during physical activity or sexual intercourse.
- Changes in Menstrual Cycle: Some women may notice alterations in their cycle, which can be linked to the cyst's presence.
- Difficulty Sitting: Bigger cysts can cause trouble while sitting down, leading to an overall discomfort.
- Infection Symptoms: If the cyst becomes infected, symptoms may escalate to include fever, increased swelling, redness, and severe pain.
The presence of these symptoms should not be overlooked, as they may indicate further issues. Early recognition of a cyst can facilitate treatment, preventing escalation into complications.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is essential to discern when to consult a healthcare professional. Some situations warrant immediate medical attention:
- Severe Pain: If a patient experiences debilitating pain that does not improve with over-the-counter medication, it is necessary to seek professional help.
- Signs of Infection: Symptoms like fever, excessive swelling, or discharge indicate that an infection may have developed, requiring urgent care.
- Persistent Cyst Growth: If a cyst continues to grow or does not resolve after a few weeks, a consultation is advisable.
- Complications Affecting Daily Life: If cyst symptoms interfere significantly with daily activities, further examination is necessary.
Seeking timely medical advice can significantly impact the outcomes for patients dealing with Bartholin cysts.
Diagnosis of Bartholin Cysts
Diagnosing Bartholin cysts is integral in establishing appropriate management and treatment plans. Early diagnosis plays a crucial role in differentiating cysts from other medical issues, such as abscesses or malignancies. A thorough understanding of the diagnostic process can aid patients and providers in identifying this condition accurately while addressing potential complications swiftly.
Physical Examination
The initial phase of diagnosis typically involves a physical examination. During this examination, a healthcare professional assesses the perineal region for any observable swelling or tenderness near the Bartholin glands. This hands-on approach allows for the identification of cysts or other abnormalities that may require further intervention. Physicians may also ask specific questions regarding recent symptoms, including any pain during intercourse or difficulties during urination.
This focused assessment assists in establishing the size and consistency of the cyst. A solid or fluctuating mass could indicate whether the cyst is filled with liquid or if it has become infected. Physical examination has practical benefits.
- It is often sufficient to diagnose uncomplicated cysts.
- It avoids unnecessary imaging tests, which can be costly and time-consuming.
- It provides immediate reassurance to the patient if the mass is benign.
Imaging Techniques
If the physical examination raises concerns or the findings are inconclusive, imaging techniques can be employed for better clarity. Typically, ultrasound emerges as the preferred method for evaluating Bartholin cysts. This non-invasive approach utilizes sound waves to create images of the internal structures.
An ultrasound can clarify the characteristics of the cyst, including its dimensions and exact location. Additionally, it can help exclude other underlying conditions that might simulate the cyst, such as tumors or an inflammation. In some cases, advanced imaging, such as MRI, may be warranted. An MRI might provide detailed insight if there is a suspicion of more complex pathology. This is particularly important if the patient has experienced recurrent cysts or significant discomfort.
In summary, the diagnosis of Bartholin cysts relies heavily on a combination of physical examinations and imaging techniques. This dual approach ensures that patients receive accurate assessments, leading to timely management. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of considering the uniqueness of each case and not relying solely on one diagnostic tool.
Conservative Treatment Options
Conservative treatment options play a crucial role in the management of Bartholin cysts. These approaches are often the first line of defense before considering surgical interventions. The benefits of conservative treatments can significantly improve quality of life for many women experiencing discomfort from cysts without the need for invasive procedures. Understanding these methods is essential for empowering patients to take control of their situation and for making informed decisions regarding their healthcare.
Observation
Observation is a common conservative approach for managing Bartholin cysts, especially in cases where symptoms are mild or absent. This method allows healthcare providers and patients to monitor the cyst without immediate action. This is particularly relevant for small cysts that do not cause pain, swelling, or other complications. Patients are encouraged to pay attention to changes in symptoms over time. It is important to consider the size of the cyst, its location, and any associated discomfort when deciding to adopt an observational approach.
The benefits of observation include:
- Avoiding unnecessary procedures. Many cysts may resolve on their own without treatment.
- Reduced risk of complications. Surgical interventions can sometimes lead to infections or other issues.
- Continuous monitoring of cyst development. Patients can identify any changes in symptoms more effectively with regular observation.
Home Remedies
Home remedies offer an alternative or complementary method for managing the discomfort associated with Bartholin cysts. While not a substitute for professional medical advice, these approaches may alleviate symptoms for some patients. Common home remedies include:
- Warm compresses. Applying a warm compress to the affected area can provide comfort and may promote drainage if the cyst is infected.
- Sitz baths. Soaking in warm water can help soothe irritation and support the healing process. A sitz bath for about 15-20 minutes can be particularly effective.
- Essential oils. Some women find relief using diluted essential oils such as tea tree or lavender oil. However, a patch test is recommended first to avoid possible irritation.
Using home remedies requires careful consideration of potential reactions. It is advisable to consult a healthcare provider before trying new methods.

"While conservative treatments can be effective, it is important to recognize when symptoms persist or worsen, as this may necessitate a more comprehensive medical evaluation."
Overall, these conservative treatment options serve as practical measures that can empower individuals managing Bartholin cysts. The importance of understanding these options cannot be overstated, as they provide avenues for symptom relief while reducing the anxiety often associated with this condition.
Medical Treatment Approaches
Medical treatment for Bartholin cysts is crucial for alleviating discomfort, managing infections, and preventing complications. Understanding the various treatment options available enables patients to make informed decisions about their health. Effective medical treatment approaches can significantly improve quality of life for those affected.
Antibiotics for Infection
Antibiotics are often prescribed when a Bartholin cyst becomes infected, leading to an abscess. This scenario requires prompt medical attention to mitigate pain and prevent further complications. Commonly used antibiotics may include:
- Ciprofloxacin
- Metronidazole
- Clindamycin
The choice of antibiotic depends on factors such as the severity of infection and potential bacterial resistance. It is vital for patients to follow the prescribed dosage and complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve prematurely. Failure to do so can lead to recurrence of the infection and could necessitate further intervention.
Proper management of infections is essential. Untreated infections can lead to more serious complications, illustrating the importance of using antibiotics as directed.
Pain Management
Pain management is another critical aspect of medical treatment for Bartholin cysts, particularly when they become inflamed or infected. Patients often experience discomfort that can range from mild to severe. Effective strategies for pain management may include:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Warm compresses: Applying a warm compress to the area can offer relief and promote drainage of the cyst if necessary.
- Topical treatments: In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend topical anesthetics to help numb the area temporarily.
It is also important for patients to communicate their pain levels with their healthcare provider, as this information can guide treatment adjustments. Understanding the individualized needs for pain management enhances the recovery process and fosters a more supportive treatment environment.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions represent a pivotal element in the management of Bartholin cysts, especially in cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief or when cysts recur frequently. Understanding when surgical options are necessary can significantly impact a patient's quality of life. Surgical procedures aim to relieve discomfort, prevent recurrence, and address potential complications associated with untreated cysts. This section discusses two primary surgical methods: marsupialization and cysts removal, along with their implications.
Marsupialization
Marsupialization is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to treat Bartholin cysts effectively. During this procedure, a small incision is made in the cyst, allowing its contents to drain. The edges of the cyst are then sutured to the vaginal wall, creating a new drainage duct. This technique is favored for its relatively simple execution and quick recovery time.
- Benefits of marsupialization include:
- Reduced recurrence rates when properly performed.
- Shorter recovery time compared to complete cyst removal.
- Ability to preserve gland function, minimizing potential complications.
Despite its advantages, marsupialization may not be suitable for all individuals, depending on cyst size and associated symptoms. Patients should discuss their specific conditions with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach.
Cysts Removal
Cysts removal, or excision, is a more extensive surgical option that involves completely removing the cyst and surrounding tissue. This procedure is generally considered when marsupialization is ineffective or if the cyst is particularly large and symptomatic. Removing the cyst may help avert further complications, such as infection or persistent discomfort.
- Key points regarding cysts removal are:
- Complete excision can lower the risk of recurrence but may carry a higher risk of complications.
- It may involve longer recovery time and an increased risk of post-operative pain.
- In some instances, this procedure may lead to the complete removal of the Bartholin gland, complicating future reproductive health.
As with all surgical procedures, a thorough evaluation and discussion of risks versus benefits should precede any decisions.
Risks and Considerations
When considering surgical options for Bartholin cysts, it is essential to be aware of potential risks and complications involved.
- Common risks include:
- Infection at the surgical site, which may complicate recovery.
- Hematoma or excessive bleeding during and after the surgery.
- Scarring, which could affect the local anatomy and possibly lead to dysfunction.
Patients should prioritize clear communication with their healthcare providers regarding their concerns and expectations. Surgical interventions can offer significant improvements in symptoms, but they require careful consideration of individual circumstances. Consulting with specialists can help tailor the approach to achieve the best outcomes while minimizing risks.
"Understanding the nuances of surgical interventions helps empower patients to make informed decisions about their treatment options."
In summary, surgical interventions play a crucial role in the comprehensive management of Bartholin cysts. Both marsupialization and cysts removal offer viable pathways for relief, but the choice hinges on specific clinical scenarios and patient preferences. As with any health-related decision, informed discussions with medical professionals are vital to navigating these options.
Aftercare and Recovery
Aftercare and recovery play a pivotal role in the overall management of Bartholin cysts. Proper aftercare ensures that patients can return to their daily activities with minimal discomfort and lower risk of complications. Understanding the significance of this phase is essential for effective recovery.
Post-Operative Care
Following surgical interventions like marsupialization or cyst removal, it is crucial to follow specific guidelines for post-operative care. This care directly influences recovery speed and comfort. Key elements include:
- Pain Management: Post-surgery, some pain or discomfort is expected. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen, can effectively manage pain. Patients should adhere to the dosage recommended by their healthcare provider.
- Hygiene Practices: Keeping the surgical area clean is vital. Patients are advised to bathe regularly and avoid using irritating products, such as scented soaps, during the early recovery phase. Daily care can prevent infection and promote healing.
- Activity Restrictions: Patients are often told to avoid strenuous activities, including heavy lifting and intense exercise, for a few weeks post-surgery. This reduces strain on the surgical site and aids in proper healing.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular check-ups with the healthcare provider help monitor the healing process. These visits allow for early intervention should issues arise.
Monitoring Symptoms
Monitoring symptoms after treatment is critical for catching potential complications early. Patients should remain vigilant about any changes in their condition. Important symptoms to track include:
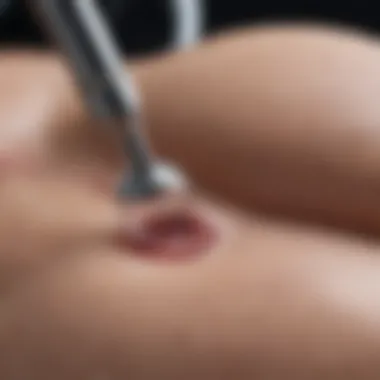
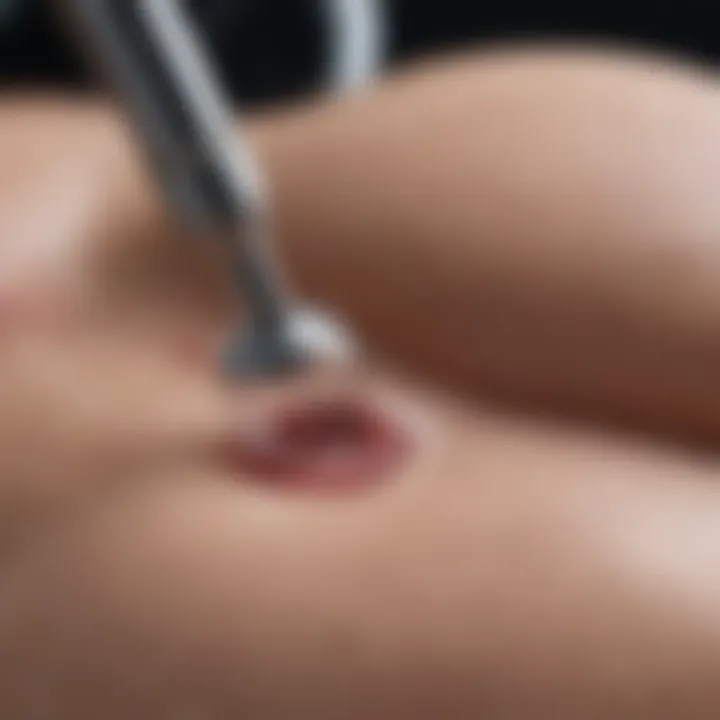
- Signs of Infection: Symptoms such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge from the surgical site should not be overlooked. If fever occurs or the pain worsens, immediate medical attention is necessary.
- Cyst Recurrence: Some patients may experience the return of cysts. Keeping a record of any new lumps or alterations in the area can be beneficial in discussing concerns during follow-up visits.
- Changes in Fluid Discharge: Any abnormal discharge from the vaginal area should be monitored. Changes in color, odor, or consistency can signal an underlying issue.
Proper aftercare is not just about healing; it significantly impacts long-term outcomes and quality of life.
Potential Complications
Understanding the potential complications of Bartholin cysts is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. This knowledge aids in recognizing the risks involved during treatment and encourages proactive management approaches. The complications may stem from the cyst itself or arise post-intervention, affecting the patient's overall well-being and quality of life.
Recurrence of Cysts
One significant concern for individuals dealing with Bartholin cysts is the possibility of recurrence. After being treated through methods such as marsupialization or cyst removal, some patients may notice the cyst returning. The recurrence rate varies but can be influenced by several factors:
- Underlying Conditions: Patients who have persistent issues that block the gland may be more prone to develop new cysts.
- Inadequate Treatment: If the initial treatment did not fully address the blockage or if some cyst material remains, recurrence is more likely.
Patients must maintain open communication with their healthcare providers, reporting any unusual changes or symptoms promptly. Engaging in regular follow-ups can help in identifying potential recurrences early, allowing for timely intervention.
Infection Risks
Infection is another critical complication that can arise from Bartholin cysts. When the cyst becomes inflamed or infected, it can lead to more severe conditions, such as abscess formation. The risk factors include:
- Hygiene Practices: Poor personal hygiene can increase the likelihood of infection.
- Delayed Treatment: Not addressing a cyst that exhibits concerning symptoms can lead to infections that complicate treatment.
Early signs of infection often include increased redness, swelling, and pain around the cyst site, along with fever. Patients should be vigilant in monitoring these symptoms and seek medical advice immediately if they arise.
Keeping informed about the potential complications related to Bartholin cysts is essential. This proactive approach can significantly enhance management and treatment outcomes.
Epilogues on Management of Bartholin Cysts
When managing Bartholin cysts, it is crucial to synthesize multiple aspects of care and treatment options. This section highlights the key benefits and considerations related to the conclusions drawn from managing these cysts. Understanding these elements allows individuals to make informed choices aimed at improving their health outcomes.
Bartholin cysts can be a source of discomfort and concern. Often, the initial step involves conservative observation, which may suffice for asymptomatic cases. This method emphasizes the importance of monitoring rather than immediate intervention. The potential for complications like infection or recurrence underscores the need for patient education and self-management strategies. By empowering patients with knowledge, they can better understand when to seek help.
Choosing between conservative and surgical options also holds significance. Each approach comes with its own set of risks and benefits. For example, surgical procedures improve symptoms but may lead to complications like scarring or recurrence. Therefore, the decision must align with individual circumstances, including cyst size, symptom severity, and personal health considerations.
Key Points for Consideration:
- The importance of regular monitoring of symptoms.
- Understanding the balance between conservative treatment and surgical intervention.
- Being aware of potential risks associated with each treatment approach.
In summary, the management of Bartholin cysts requires a comprehensive understanding of the condition and careful consideration of treatment options. It is vital for patients to engage actively in their care, promoting favorable outcomes and reducing anxiety related to their condition.
Empowering Patients
Empowerment in the context of Bartholin cyst management means equipping individuals with essential knowledge and tools. Patients need to feel confident in their ability to recognize symptoms and make informed decisions about their health. This section emphasizes the significance of education in the management process.
When patients understand their condition, they are more likely to participate actively in their treatment plans. Being educated about treatment options, potential side effects, and the signs of complications encourages timely intervention. This sense of control can alleviate some of the fear associated with having a Bartholin cyst.
Furthermore, community resources and support groups can play an important role in this empowerment. Discussions with others who share similar experiences can provide valuable insights and emotional support. Online platforms, such as discussions on Reddit or Facebook groups, create spaces for sharing knowledge and experiences.
Future Directions in Treatment
Research in the field of gynecology continues to evolve, paving the way for more effective and less invasive treatment options for Bartholin cysts. Future directions might include advances in minimally invasive surgical techniques or the development of targeted therapies that reduce cyst formation and recurrence.
Telemedicine is also likely to reshape how patients access care. Virtual consultations offer convenience and can facilitate quicker, less stressful encounters with healthcare professionals. Technological improvements may create opportunities for continuous monitoring and management of benign conditions like Bartholin cysts from the comfort of home.
Overall, the future of treating Bartholin cysts seems promising, with evolving methodologies that emphasize patient comfort and health outcomes. As research progresses, there will be more options available to manage these cysts effectively, allowing individuals to lead healthier lives.
References and Further Reading
Understanding Bartholin cysts involves delving into a wide array of scholarly articles, studies, and resources that illuminate various aspects of this condition. References and further reading not only provide depth to the topic but also empower individuals and professionals by grounding their knowledge in rigorous scientific research.
In our age of information, it is vital to distinguish quality sources that enhance understanding. Here are some significant points about why references and further reading are important:
- Credibility: Reliable sources, such as scholar articles, lend credibility to the information presented. High-quality references help ensure that the reader receives accurate and meaningful content.
- Depth of Knowledge: Engaging with diverse materials allows readers to explore complex topics thoroughly. Academic publications usually possess greater detail than articles aimed at a general audience.
- Continued Learning: The field of medicine, including conditions like Bartholin cysts, is constantly evolving. Staying updated through current literature enables a better grasp of advancements and changes in treatment approaches.
Scholar Articles
Scholarly articles serve as the backbone of medical research and understanding. These documents undergo rigorous peer review, ensuring that they meet high standards of scientific inquiry. For Bartholin cysts, specific articles can guide readers on numerous subtopics, such as pathophysiology, management strategies, and long-term outcomes.
When looking for valuable scholar articles, consider these features:
- Relevance: Choose articles focused on Bartholin cysts or closely related topics to gain targeted insights.
- Recent Publications: Prioritize articles published in the last five years to ensure the content reflects current understanding.
- Author Credentials: Examine the backgrounds of authors to ascertain their expertise in the field.
Some significant platforms where these articles can be found include:
- PubMed
- Google Scholar
- ResearchGate
Online Resources
Online resources provide a wealth of information that is often easier to digest than traditional academic texts. They can assist both patients and healthcare professionals in understanding Bartholin cysts and their management.
Key online resources include:
- Trusted Medical Websites: Sites like en.wikipedia.org and britannica.com offer foundational knowledge and are usually well-verified.
- Health Organizations: Websites of reputable health organizations often provide patient education material, symptom checkers, and treatment guidelines.
- Forums and Communities: Platforms like reddit.com and specific Facebook groups can offer personal experiences and tips, but it is crucial to approach these with caution. Always cross-reference information with verified medical sources to ensure accuracy.
Engaging with a mixture of scholarly articles and online resources allows for a comprehensive understanding of Bartholin cysts and equips readers with the tools they need for informed decision-making.















