Vein Embolization Procedure: Detailed Insights
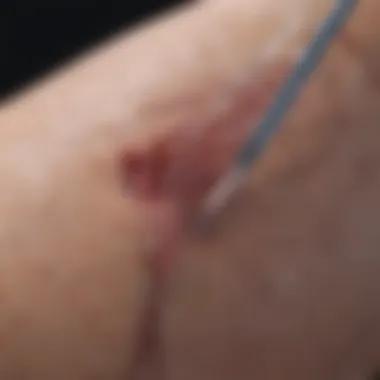

Intro
Vein embolization stands at the forefront of modern medical interventions aimed at managing various venous disorders. In recent years, this procedure has garnered significant interest due to its effectiveness and minimally invasive approach. By understanding what vein embolization entails, we can appreciate its role within the broader context of venous health and treatment options available today.
This procedure identifies and intentionally obstructs problematic veins, directing blood flow towards healthier vessels.
What is Vein Embolization?
At its essence, vein embolization is a minimally invasive procedure used primarily to treat conditions such as varicose veins, venous malformations, and even certain instances of deep vein thrombosis. During the procedure, a small catheter is inserted into the affected vein. Through this catheter, various materials are deployed to obstruct the troublesome vein. These materials can include:
- Sclerosing agents—liquids that cause the vein to scar and close.
- Coils—small metallic spirals that physically block the vein.
- Glue—adhesive substances that fuse the vein walls together.
The choice of embolic material often depends on the specific condition being treated, underscoring the importance of a tailored approach.
Purpose of Vein Embolization
The primary purpose of this procedure is to alleviate symptoms associated with venous disorders. These may range from discomfort and swelling to more severe complications such as bleeding or skin ulcers. By occluding the problematic veins, vein embolization not only reduces symptoms but can also prevent further complications down the line.
Summary of Objectives
The findings of this examination will delve into the various facets of the vein embolization procedure. We will explore its indications, techniques involved, risks associated with the procedure, and postoperative care recommendations. The aim is to foster a comprehensive understanding among healthcare professionals and patients alike, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding treatment options.
Importance of the Research
By shedding light on vein embolization, we open pathways to enhanced patient care and better health outcomes. As medical technology continues to evolve, understanding the nuanced aspects of such procedures becomes crucial. This overview will serve as a stepping stone for ongoing discussions and research in the field of vascular health.
Intro to Vein Embolization
Vein embolization is not just a medical procedure; it embodies a significant leap forward in vascular treatment, specifically addressing venous disorders that often affect individuals’ quality of life. It's essential to unpack this topic, as understanding vein embolization can illuminate the path to better health for many struggling with chronic problems like varicose veins or venous insufficiency. Compared to traditional surgical methods, vein embolization offers less invasive solutions with reduced recovery times and lower rates of complications. In an era where patient comfort and quick recovery are pivotal, this procedure is gaining ground.
Definition of Vein Embolization
So, what exactly is vein embolization? In layman's terms, it's a procedure meant to block off, or embolize, specific veins to treat various conditions, portrayed mainly by symptoms like swelling or discomfort in the legs. A healthcare provider employs a catheter to deliver substances that either harden or block the targeted vein. This effectively reroutes blood flow to healthier veins without needing major surgery. This all sounds quite straightforward, but it encompasses a range of techniques and technologies designed to tailor treatment to individual patient needs.
Historical Context
The journey of vein embolization is rooted in innovation. Initially, vascular treatments were rather rudimentary. Ancient methods involved practices that seem almost primitive by today's standards, such as cauterization. Fast forward to the late 20th century, where significant advancements in imaging and catheter technology began to emerge. Over the past few decades, vein embolization has evolved from a niche procedure to a well-accepted, evidence-based intervention. With decades of research backing its efficacy and safety, this method stands tall in the arsenal of vein treatment options.
Many medical professionals, eager to provide their patients with modern solutions, have embraced this procedure wholeheartedly. By understanding its evolution, we can appreciate not just its current role in managing vascular disorders but also the rigorous journey that brought us here. In this exploration, we’ll delve into the intricacies of the procedure, from indications through techniques, risks, and outcomes, to truly appreciate how vein embolization is reshaping vascular medicine.
Indications for the Procedure
The vein embolization procedure plays a pivotal role in managing various venous disorders, and understanding the indications is key to recognizing its importance in modern medicine. This section delves into the specific conditions warranting this intervention, aiming to shed light on the significant benefits the procedure offers to patients. The correct identification of indications ensures optimal patient outcomes and helps healthcare providers make informed decisions that align with both medical guidelines and patient needs.
Varicose Veins Management
Varicose veins are often seen as a mere cosmetic concern, but they can lead to considerable discomfort and complications. These bulging veins, often appearing blue or dark purple, can signal underlying venous insufficiency or contribute to painful symptoms like swelling and aching. Managing varicose veins through vein embolization not only addresses aesthetic concerns but also alleviates discomfort and reduces long-term complications. The procedure can effectively close off problematic veins, directing blood flow to healthier vessels and minimizing the likelihood of recurrence.
Patients often consider vein embolization when other conservative treatments, such as compression therapy or lifestyle adjustments, fail to yield satisfactory results. The following are key points regarding varicose veins management through vein embolization:
- Immediate relief: Patients typically experience significant symptom improvement soon after the procedure.
- Minimally invasive: The procedure often requires less downtime compared to traditional surgical options.
- Aesthetic outcomes: Many patients report satisfaction with the visual improvement of their legs post-treatment.
Treatment of Venous Insufficiency
Venous insufficiency occurs when veins struggle to return blood to the heart, resulting in pooling and pressure build-up in the leg veins. This condition can lead to several complications, including chronic pain, skin changes, and even ulceration. Vein embolization is an effective treatment option, particularly when conservative measures like medications or compression stockings don’t provide lasting relief.
By closing off malfunctioning veins, vein embolization enhances venous circulation, leading to improved blood flow in the legs. The treatment is suitable for various degrees of venous insufficiency, making it a flexible option. Here’s why vein embolization stands out in treating this condition:
- Targeted approach: The procedure directly addresses the specific veins involved in the insufficiency.
- Potential for less scarring: As a minimally invasive method, it typically results in smaller scars than traditional surgical techniques.
- Cost-effective: Patients often see reduced long-term medical costs due to fewer complications and an improved quality of life.
Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) refers to the formation of blood clots in the veins, which can have serious consequences if not addressed promptly. Patients at high risk for VTE include those with a history of deep vein thrombosis, recent surgery, or prolonged immobility. Preventing VTE is crucial, and vein embolization can serve as a preventative measure for certain patients.
For instance, in cases where other prophylactic measures are insufficient or not well tolerated, vein embolization can reduce the venous stasis that contributes to clot formation. Important considerations include:
- Assessment of risk factors: Identifying patients with a heightened risk of VTE is paramount to implementing preventive strategies effectively.
- Integration with other preventive measures: Embolization works best in conjunction with other treatments, such as anticoagulants.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-ups can help track the success of the prevention strategy and make necessary adjustments.


Vein embolization offers a multifaceted approach to managing venous disorders, addressing not only the symptoms but also the root causes and complications associated with vein diseases. In doing so, it enhances not just patient health outcomes but ultimately their quality of life.
Underlying Anatomy and Pathophysiology
Understanding the complex framework of the venous system and the disorders that can disrupt it is crucial for grasping the implications of the vein embolization procedure. This section delves into key anatomical features and the pathophysiological changes that inform treatment strategies. Without a solid comprehension of how veins function and the challenges they face, healthcare professionals may struggle to make informed decisions that optimize patient outcomes. Therefore, an in-depth examination of venous anatomy and related disorders provides a foundation for appreciating the rationale behind embolization interventions.
Venous Anatomy Overview
The venous system primarily consists of a network of veins responsible for returning deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Key structures include:
- Superficial Veins: Located close to the skin surface, these veins are often involved in conditions like varicose veins, where they become dilated and tortuous.
- Deep Veins: Found deeper in the limbs, these veins are crucial for efficient blood return, often impacted by conditions like deep vein thrombosis.
- Valves: One-way valves within veins prevent retrograde flow, ensuring blood ascends toward the heart.
- Venous Sinuses: Special spaces that collect blood, particularly in the cranial cavity and heart.
Each component plays a role in systemic circulation and its dysfunction can lead to significant clinical problems. For instance, compromised valves can result in venous reflux, a scenario where blood flows backward due to valve failure, manifesting as symptoms like swelling and pain.
Venous Disorders and Their Impact
Venous disorders can have a profound impact on an individual's health and quality of life. These conditions can range from benign to life-threatening, and their repercussions are broad, affecting physical, emotional, and social well-being.
- Varicose Veins: These are perhaps the most notorious of venous disorders, commonly seen as swollen and blue veins, especially in the legs. They not only pose an aesthetic concern but can also lead to discomfort and complications like ulcers.
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency: A more severe condition where the veins cannot efficiently return blood to the heart, leading to swelling, pain, and skin changes. This disorder can come with significant morbidity, as untreated cases may progress to skin infections and other complications.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): This is a serious condition where blood clots form in deep veins, primarily in the legs. DVT can lead to life-threatening pulmonary embolism when clots dislodge and travel to the lungs.
"Understanding the underpinning anatomy and associated disorders not only aids in selecting appropriate interventions but also enhances patient education, allowing individuals to grasp the significance of proposed treatments like vein embolization."
Procedure Techniques
Understanding the process of vein embolization is not just about knowing the end result; it’s vital to grasp the procedural techniques that lead to successful outcomes. This section outlines the core steps involved, from meticulous preparation to the introduction of specific embolic agents. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring that the procedure is not only effective but also minimizes risks associated with it.
Preparation and Planning
Preparation lays the groundwork for a successful vein embolization. Before even considering the procedure, thorough patient evaluation is critical. This includes a review of the patient's medical history, imaging studies to visualize vein structure, and a discussion around the patient's symptoms.
The ultimate goals during this preparatory phase are to:
- Assess the specific venous disorder affecting the patient.
- Determine eligibility for embolization based on clinical findings.
- Outline the procedure's steps to ensure patient understanding and cooperation.
Furthermore, it often involves collaboration among healthcare professionals, including radiologists and vascular surgeons. This interdisciplinary approach guarantees that all angles are covered and that the strategies employed are tailored to individual patient needs.
Catheter Placement Techniques
Once the stage is set in the preparatory phase, attention turns to the actual placement of the catheter, which is an essential step in the embolization process. Typically, insertion sites include the femoral or jugular veins, chosen for their anatomical advantages.
Healthcare professionals utilize advanced imaging techniques to guide the catheter through the vascular pathways. A few vital points regarding catheter placement include:
- Catheter types vary, with options like the coaxial system proving popular due to their flexibility.
- Fluoroscopy or ultrasound assists in accurate navigation within the venous system, providing real-time visuals that enhance precision.
- Positioning is crucial: correct placement directly impacts the effectiveness of the embolization.
In this phase, it's also important to monitor for immediate complications during catheter placement, ensuring that any issues are addressed promptly to reduce the likelihood of adverse events.
Embolic Agents Utilized
The selection of embolic agents is a pivotal element in the vein embolization process. Various materials are used based on the desired outcome and the nature of the venous disorder. Common embolic agents include:
- Sclerosants: These agents promote fibrosis and are often used for small veins, leading to their closure and subsequent absorption.
- Gels or particles: Larger veins may require particulate agents that occlude the vessel, cutting off blood flow effectively.
- Coils: These are often used in larger vessels, providing a physical barrier that catalyzes clot formation.
Selecting the appropriate agent involves a careful consideration of the patient’s diagnosis and treatment goals. This choice also comes with a thorough understanding of potential side effects, ensuring that patients are informed about what to expect during and after the procedure.
"The success of vein embolization hinges not just on the technique, but on meticulous planning and the right choice of materials."
In sum, the procedural techniques of vein embolization include critical stages of preparation, catheter placement, and the selection of embolic agents. Each of these steps ensures that the intervention is tailored effectively to the needs of the patient while minimizing potential risks. The meticulous nature of these techniques reflects their importance in achieving optimal patient outcomes.
Risks and Complications
Understanding the Risks and Complications associated with vein embolization is pivotal in fully grasping the procedure's implications for patient health. This segment sheds light on what patients might face not just in the immediate aftermath of the surgery but also in the long run. By examining these elements, healthcare professionals can better prepare patients and aid them in navigating their recovery journey.
Immediate Post-Procedure Risks
Upon waking from the procedure, patients may find themselves facing a handful of immediate risks. These potential complications could vary in severity, and while some might be minor, others could necessitate swift intervention.
Common immediate risks include:
- Pain and Discomfort: Post-procedure, patients often report localized pain where the catheter was inserted. This discomfort can range from mild to moderate.
- Bleeding: Though it doesn’t occur frequently, it’s essential to monitor for any excessive bleeding at the insertion site.
- Infection: The risk for infection exists whenever the skin barrier is breached. Keeping the area clean is crucial to mitigate this risk.
- Allergic Reactions: Reactions to anesthetics or the contrast dye used during the procedure, though rare, warrant caution.


Being aware of these immediate post-procedure risks aids patients in understanding what symptoms to monitor and when to seek further assistance.
Long-Term Complications
As with many medical procedures, vein embolization can come with its share of long-term complications. Even though many patients experience significant relief from their symptoms, being cognizant of possible issues can help in early detection and treatment.
Some long-term complications may include:
- Recurrence of Symptoms: Some individuals may experience a return of varicose veins or symptoms associated with venous insufficiency.
- Chronic Pain: Over time, some patients may develop a condition known as post-thrombotic syndrome, which can lead to lasting discomfort.
- Hyperpigmentation: Darkening of the skin can occur in some individuals as a result of blood pooling or other factors after the procedure.
Identifying these long-term risks ensures that patients are not caught off guard if they begin to experience new or returning symptoms after the procedure. It also allows them to have open dialogues with their healthcare providers about their concerns.
Management of Complications
When complications arise from vein embolization, it is essential to have a management strategy in place. Addressing these complications swiftly can significantly improve overall patient outcomes. Strategies for managing complications can be categorized as follows:
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular follow-ups after the procedure can help in identifying problems early.
- Medications: Prescribing pain relief medications or other drugs to manage symptoms can be effective in treating complications.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Encouraging patients to adopt certain lifestyle changes may alleviate or mitigate some complications. This could include regular exercise or wearing compression stockings.
- Surgical Interventions: In serious cases, further surgical procedures may sometimes be necessary to correct or address complications arising from the embolization.
The importance of proper management cannot be overstated; it is essential for ensuring the best possible outcomes.
"A stitch in time saves nine." Recognizing these risks and complications allows patients to take proactive steps in their health journey.
Outcomes of the Vein Embolization Procedure
The results following vein embolization are critical in understanding its overall effectiveness and long-term viability as a treatment option for venous disorders. By assessing patient outcomes, healthcare professionals can gauge the procedure’s success and refine future practices. Key elements that underline the importance of these outcomes include their impact on both physical health and quality of life.
The outcomes of the vein embolization procedure are generally grouped into short-term patient outcomes and long-term success rates. Each offers distinct insights into the effectiveness of the method, the experiences of patients, and the potential future of venous disorder management.
Short-Term Patient Outcomes
In the immediate aftermath of the vein embolization procedure, patients typically experience a range of outcomes that can significantly influence the trajectory of their recovery. Common variables include pain levels, swelling, and overall satisfaction with treatment. Most patients report a noticeable decrease in symptoms associated with conditions like varicose veins soon after the procedure.
Some of the key short-term outcomes often observed include:
- Pain Relief: Many individuals report reduced pain levels just days after the embolization procedure, marking a significant improvement in their condition.
- Swelling Reduction: The procedure often leads to decreased swelling of the affected area, which can enhance mobility and comfort.
- Satisfaction Rates: A good number of patients express satisfaction with the results shortly after the procedure, contributing to a positive perception of vein embolization.
These indicators contribute to a crucial aspect of patient care—ensuring that the individual feels rejuvenated physically and emotionally. It is essential, however, to note that not every patient will have the same experience. Variations in individual health factors and adherence to post-operative care can affect these outcomes.
Long-Term Success Rates
When evaluating the long-term success of vein embolization, various studies suggest a promising outlook. Long-term results can provide reassurance not only to patients but also to healthcare providers regarding the sustainability of the treatment. Key metrics include:
- Recurrence Rates: Research shows that the rates of recurrence for symptoms post-procedure tend to be low, often under 10% within the first few years following treatment.
- Improved Quality of Life: Many patients continue to report enhancements in their quality of life long after the procedure, which can be attributed to sustained symptom relief.
- Durability of Results: Longitudinal studies indicate that the improvements achieved through vein embolization can last for several years, making it an effective long-term solution for managing venous disorders.
In essence, the effectiveness of vein embolization as a viable treatment is underscored by its positive long-term outcomes, offering patients durable relief from their symptoms and improving their overall well-being.
The overall narrative suggests that while short-term results are encouraging, it is the long-term success rates that provide the backbone for the continued recommendation of vein embolization to patients dealing with venous disorders. This insight aligns with ongoing research that seeks to further enhance procedural techniques and outcomes, incorporating patient experiences into future developments.
Postoperative Care and Monitoring
Postoperative care and monitoring are critical to ensuring the overall success of the vein embolization procedure. After the intervention, patients may experience a range of effects which need careful management. Proper postoperative protocols can significantly improve healing times and minimize complications. Effective monitoring not only allows for early detection of issues but also instills confidence in the patient regarding their recovery.
Immediate Aftercare Protocol
The immediate aftercare protocol is initiated right after the vein embolization procedure is completed. It focuses on several key elements to ensure that patients return to optimal health without unnecessary hiccups.
- Patient Observation: Right after the procedure, patients are usually kept under observation for a few hours to monitor for any adverse reactions. Nursing staff checks vital signs frequently to ensure stability.
- Pain Management: While discomfort is common, excessive pain should not be tolerated. Healthcare providers typically prescribe medications to manage pain effectively.
- Compression Garments: Applying compression garments may be necessary as it helps to reduce swelling and supports the healing process. Patients are informed about the proper usage of these garments.
- Activity Restrictions: Patients are advised to avoid heavy physical activities for at least a week. Light walking is encouraged as it aids in circulation without overexerting the body.
- Hydration and Diet: Maintaining hydration is essential. Patients are encouraged to drink plenty of fluids and to follow a balanced diet to promote recovery.
Follow-Up Assessments
Follow-up assessments play an important role in ensuring that the vein embolization procedure has yielded the desired outcomes. These evaluations help in managing recovery and in addressing any lingering issues.
- Scheduled Appointments: Typically, follow-up visits are arranged a week or two post-procedure. During these appointments, healthcare providers assess the injection site for any signs of complications such as infection or excessive swelling.
- Ultrasound Imaging: Many practitioners perform ultrasound imaging during follow-ups. This helps to evaluate the blood flow in the treated areas and to ensure that the veins are functioning effectively.
- Patient Feedback: Gathering insights from patients about their comfort levels and any lingering symptoms is crucial. This feedback can help healthcare providers make informed decisions about follow-up care.
Effective postoperative care is key in avoiding complications and ensuring a smooth recovery, leading to the best possible outcomes in vein embolization.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Depending on individual cases, longer-term monitoring such as annual check-ups may be needed. This is particularly true for those who had significant venous disorders to ensure that they do not recur.
In essence, both immediate aftercare and structured follow-up are not just procedural formalities; they comprise an integral portion of the vein embolization process. Giving due attention to these steps can have a considerable positive impact on a patient’s overall journey towards recovery.

Future Directions in Vein Embolization
The field of vein embolization is witnessing a dynamic shift as technologies advance and research unveils deeper layers of understanding about venous disorders. As practitioners and patients alike look towards effective solutions, it becomes vital to explore the promising pathways that lie ahead for this procedure. Through integration of cutting-edge technology and ongoing research efforts, vein embolization is poised to transform into an even more compelling option for managing venous conditions.
Technological Advancements
Technological innovations are the backbone of modern medical procedures, and vein embolization is no exception. Some advancements that stand out in this regard include:
- Enhanced Imaging Techniques: The use of real-time imaging such as ultrasound and fluoroscopy provides clearer anatomical details, making it easier for surgeons to locate and identify problem areas during the embolization. This precision reduces risks and improves overall outcomes.
- Advanced Embolic Materials: Developments in the types of materials used for embolization have accelerated progress. Novel agents like bioresorbable microspheres not only facilitate the occlusion of veins but also minimize long-term complications associated with permanent materials.
- Automation in Procedures: Robotics and AI-assisted technologies are beginning to influence how these procedures are performed. Automation reduces the variability in techniques, enhancing consistency and potentially leading to better patient outcomes.
The embrace of such advancements reshapes how vein embolization is performed. It opens a new world of possibilities that could lead to less invasive procedures and quicker recovery times for patients.
Research Implications
The research landscape surrounding vein embolization is evolving rapidly, yielding insights that can significantly shift treatment paradigms.
- Longitudinal Studies: Ongoing studies aiming to follow patients over extended periods will provide critical data on the long-term effectiveness of embolization. This research might clarify how different techniques and materials impact outcomes and recovery times, guiding future clinical practices.
- Comparative Effectiveness Research: This type of research will play a vital role in understanding how vein embolization pairs against other treatment modalities for venous disorders. Through randomized control trials and retrospective studies, clinicians will be positioned to make informed decisions that enhance patient care.
- Patient-Centric Approaches: There's an increasing focus on understanding the patient experience through qualitative research. Insights regarding postoperative quality of life and satisfaction can inform techniques and approaches, ensuring alignment with patient expectations and improving adherence to treatment regimens.
Research impacts clinical practice, and as the findings gather momentum, they may influence standard protocols and elevate patient care in vein embolization.
Overall, the trajectory of vein embolization reflects a convergence of innovative technology and robust research efforts, signaling a bright future for this medical intervention.
"The future belongs to those who believe in the beauty of their dreams." - Eleanor Roosevelt
As we dream and plan for advancements in vein embolization, we must acknowledge the potential waiting just around the corner.
Patient Considerations and Decision-Making
In the realm of vein embolization, patient considerations and decision-making play a pivotal role. Understanding the intricacies of this procedure allows patients to have meaningful dialogues with their healthcare providers. It involves not just the technical aspects but also the emotional and psychological dimensions of choosing treatment.
The decision-making process should be patient-centered, focusing on several essential elements:
- Individual Health Status: Each patient's health can dramatically influence treatment options. Factors such as age, chronic illnesses, or previous surgeries must all be taken into account before proceeding with vein embolization.
- Informed Consent: Patients should be fully informed about the procedure itself, potential risks, benefits, and alternatives. This knowledge empowers them to make well-rounded choices.
- Personal Values and Goals: A patient’s lifestyle, daily activities, and personal beliefs regarding health care can significantly shape their willingness to undergo a medical intervention.
- Post-Procedure Expectations: Understanding what the aftermath of the procedure may look like, including recovery time and any possible lifestyle changes.
In summary, the balance between the desire for recovery and the apprehension about what the procedure entails should guide the patient in their decision-making process.
Informed Consent Process
The informed consent process is a cornerstone of medical ethics and is especially critical in vein embolization. This phase is designed to ensure that patients are fully aware of what they are agreeing to. A healthcare provider must explain:
- The Procedure: What vein embolization involves, stepped out clearly so there's no room for misunderstanding.
- Possible Risks and Benefits: Both short-term and long-term effects, allowing patients to weigh the pros and cons accurately.
- Alternatives Available: Discussing non-invasive or less invasive options provides a broader view and addresses patient concerns.
While the discussion may feel daunting, it’s vital. A patient’s comfort with their healthcare provider can lead to a more fruitful consent process.
“Informed consent isn’t just a form; it’s a dialogue.”
Quality of Life Post-Procedure
Post-procedure quality of life is an essential consideration for patients contemplating vein embolization. It’s not just about the procedure’s success—what happens afterwards has a significant impact.
Following vein embolization, many patients experience varying degrees of improvements:
- Reduction of Symptoms: Patients often notice a decrease in pain or discomfort, which markedly enhances daily functioning.
- Improved Mobility: Many find their ability to engage in physical activities restored, leading to better overall health.
- Psychological Benefits: A transformation in how one feels about their body can lead to heightened self-esteem and reduced anxiety, significantly affecting mental well-being.
Evaluating these aspects can help patients understand that the benefits extends beyond mere appearance; it lays groundwork for a healthier lifestyle. Proper support systems must also be in place post-procedure to ensure smooth recuperation.
The End and Summary Insights
The vein embolization procedure serves as a critical treatment option for various venous disorders, significantly impacting patient quality of life. Understanding its implications is essential for not only medical providers but also for patients contemplating this intervention. It is vital to recognize the balance between the advantages it presents, such as reduced symptoms of venous insufficiency and diminished risks of complications like thrombosis, against the possible drawbacks like post-procedure pain or infection. By distilling this knowledge, both healthcare professionals and prospective patients are better equipped to make informed decisions.
Recap of Key Points
In this article, we explored several pivotal aspects of vein embolization:
- Definition and Historical Context: Outlining what vein embolization entails and tracing its evolution as a therapeutic option.
- Indications for the Procedure: Understanding when this intervention is recommended, particularly in cases of varicose veins, venous insufficiency, and thromboembolism prevention.
- Underlining Techniques and Risks: A detailed look at how the procedure is performed, including the inherent risks associated with it.
- Postoperative Care and Future Directions: Emphasizing the significance of attentive aftercare and the exciting prospects for advancements in techniques and technologies.
This recap not only summarizes the pillars of vein embolization but also highlights its growing relevance in the field of vascular medicine.
The Role of Vein Embolization in Modern Medicine
Vein embolization has carved out its niche in the realm of modern medical practice, addressing a crucial need for effective management of venous insufficiencies. Its application represents a shift towards minimally invasive techniques that facilitate faster recovery and less disruption to patients' daily lives. Moreover, the evolving landscape of this procedure underscores its adaptability; with ongoing research, newer materials and technologies continue to emerge, enhancing both safety and efficacy.
Overall, vein embolization is more than just a procedure; it signifies a broader commitment to advancing patient care in vascular health. As new data surface, its role in treatment protocols is likely to expand, potentially leading to even greater successes in managing complex venous disorders.
"Vein embolization exemplifies the intersection of innovation and patient-centered care, spotlighting the trajectory of contemporary vascular treatments."
This dynamic nature of the procedure not only speaks volumes about its importance in addressing venous diseases but also invites a continued dialogue in the medical community regarding best practices and innovations that could shape the future of vascular treatments.















